-
乙酸乙酯
NMR and HPLC COA下载 MSDS下载 - Names:
Ethylacetate
- CAS号:
141-78-6
MDL Number: MFCD00009171 - MF(分子式): C4H8O2 MW(分子量): 88.11
- EINECS:205-500-4 Reaxys Number:506104
- Pubchem ID:24856422 Brand:BIOFOUNT
| 货品编码 | 规格 | 纯度 | 价格 (¥) | 现价(¥) | 特价(¥) | 库存描述 | 数量 | 总计 (¥) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JG0083-1L | 1L | 99.8%,Water≤50 ppm (by B.F.), B.FSeal | ¥ 678.00 | ¥ 678.00 | 3-5days | ¥ 0.00 | ||
| JG0083-500ml | 500ml | 99.8%,Water≤50 ppm (by B.F.), B.FSeal | ¥ 458.00 | ¥ 458.00 | 3-5days | ¥ 0.00 | ||
| JG0083-100ml | 100ml | 99.8%,Water≤50 ppm (by B.F.), B.FSeal | ¥ 228.00 | ¥ 228.00 | 3-5days | ¥ 0.00 |
| 中文别名 | 乙酸乙酯(141-78-6),醋酸乙酯; |
| 英文别名 | Ethylacetate(141-78-6);Ethylacetate,Acetidin; Vinegar naphtha; Ethyl ethanoate; Ethyl acetic ester; Ethyl acetate; Acetoxyethane; Ethylacetate; Acetic ether; Acetic acid ethyl ester; |
| CAS号 | 141-78-6 |
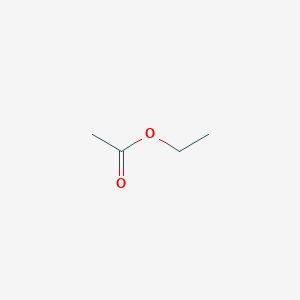
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C |
| Inchi | InChI=1S/C4H8O2/c1-3-6-4(2)5/h3H2,1-2H3 |
| InchiKey | XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| 分子式 Formula | C4H8O2 |
| 分子量 Molecular Weight | 88.11 |
| 闪点 FP | -3 °C |
| 熔点 Melting point | -83°C |
| 沸点 Boiling point | 77°C |
| Polarizability极化度 | 8.9±0.5 10-24cm3 |
| 密度 Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
| 蒸汽压 Vapor Pressure | 111.7±0.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| 溶解度Solubility | 80 g/L (20 oC) |
| 性状 | No data available |
| 储藏条件 Storage conditions | 2-8°C,Store at 4°C,-4℃下存储更优 |
乙酸乙酯(141-78-6,Ethylacetate)毒理性质:
| 生物 | 测试类型 | 路线 | 报告剂量(标准化剂量) | 影响 | 资源 |
| cat | LCLo | inhalation | 61gm/m3 (61000mg/m3) | "Handbook of Toxicology," 4 vols., Philadelphia, W.B. Saunders Co., 1956-59Vol. 1, Pg. 336, 1955. | |
| cat | LD50 | subcutaneous | 3gm/kg (3000mg/kg) | BLOOD: OTHER CHANGES | Archiv fuer Gewerbepathologie und Gewerbehygiene. Vol. 5, Pg. 1, 1933. |
| BEHAVIORAL: SOMNOLENCE (GENERAL DEPRESSED ACTIVITY) | |||||
| GASTROINTESTINAL: NAUSEA OR VOMITING | |||||
| guinea pig | LD50 | oral | 5500mg/kg (5500mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: COMA | Gigiena i Sanitariya. For English translation, see HYSAAV. Vol. 48(4), Pg. 66, 1983. |
| BEHAVIORAL: CHANGES IN MOTOR ACTIVITY (SPECIFIC ASSAY) | |||||
| BEHAVIORAL: SOMNOLENCE (GENERAL DEPRESSED ACTIVITY) | |||||
| guinea pig | LD50 | subcutaneous | 3gm/kg (3000mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: SOMNOLENCE (GENERAL DEPRESSED ACTIVITY) | Archiv fuer Gewerbepathologie und Gewerbehygiene. Vol. 5, Pg. 1, 1933. |
| human | TCLo | inhalation | 400ppm (400ppm) | SENSE ORGANS AND SPECIAL SENSES: OTHER CHANGES: OLFACTION | Journal of Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology. Vol. 25, Pg. 282, 1943. |
| LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: OTHER CHANGES | |||||
| SENSE ORGANS AND SPECIAL SENSES: CONJUNCTIVE IRRITATION: EYE | |||||
| mouse | LC50 | inhalation | 45gm/m3/2H (45000mg/m3) | "Toxicometric Parameters of Industrial Toxic Chemicals Under Single Exposure," Izmerov, N.F., et al., Moscow, Centre of International Projects, GKNT, 1982Vol. -, Pg. 65, 1982. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 709mg/kg (709mg/kg) | Shell Chemical Company. Unpublished Report. Vol. -, Pg. 5, 1961. | |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 4100mg/kg (4100mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: SOMNOLENCE (GENERAL DEPRESSED ACTIVITY) | Gigiena i Sanitariya. For English translation, see HYSAAV. Vol. 48(4), Pg. 66, 1983. |
| BEHAVIORAL: CHANGES IN MOTOR ACTIVITY (SPECIFIC ASSAY) | |||||
| BEHAVIORAL: COMA | |||||
| rabbit | LD50 | oral | 4935mg/kg (4935mg/kg) | Industrial Medicine and Surgery. Vol. 41, Pg. 31, 1972. | |
| rabbit | LD50 | skin | > 20mL/kg (20mL/kg) | Union Carbide Data Sheet. Vol. 10/4/1968, | |
| rat | LC50 | inhalation | 200gm/m3 (200000mg/m3) | GASTROINTESTINAL: CHANGES IN STRUCTURE OR FUNCTION OF SALIVARY GLANDS | Science Reports of the Research Institutes, Tohoku University, Series C: Medicine. Vol. 36(1-4), Pg. 10, 1989. |
| LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: ACUTE PULMONARY EDEMA | |||||
| BEHAVIORAL: SOMNOLENCE (GENERAL DEPRESSED ACTIVITY) | |||||
| rat | LD50 | oral | 5620mg/kg (5620mg/kg) | Yakkyoku. Pharmacy. Vol. 32, Pg. 1241, 1981. | |
| rat | LDLo | subcutaneous | 5gm/kg (5000mg/kg) | Bolletino della Societe Italiana di Biologia Sperimentale. Vol. 18, Pg. 45, 1943. |
乙酸乙酯(141-78-6,Ethylacetate)实验注意事项:
1.使用141-78-6实验前需戴好防护眼镜,穿戴防护服和口罩,佩戴手套,避免与皮肤接触。
2.使用141-78-6实验过程中如遇到有毒或者刺激性物质及有害物质产生,必要时实验操作需要手套箱内完成以免对实验人员造成伤害。
3.取样品141-78-6的移液枪头需及时更换,必要时为避免交叉污染尽可能选择滤芯吸头。
4.称量药品时选用称量纸,并无风处取药和称量以免扬撒,试剂的容器使用前务必确保干净,并消毒。
5.取药品141-78-6时尽量采用多个药勺分别使用,使用后清洗干净。
6.实验后产生的废弃物需分类存储,并交于专业生物废气物处理公司处理,以免造成环境污染。
大规格定制:定制产品请将信息发送至sales@bio-fount.com。
Experimental considerations:
1. Wear protective glasses, protective clothing and masks, gloves, and avoid contact with the skin during the experiment.
2. The waste generated after the experiment needs to be stored separately, and handed over to a professional biological waste gas treatment company to avoid environmental pollution.
Tags:乙酸乙酯试剂,乙酸乙酯杂质,乙酸乙酯中间体,乙酸乙酯合成,乙酸乙酯闪点,乙酸乙酯溶解度,乙酸乙酯旋光度,乙酸乙酯结构式,乙酸乙酯购买,乙酸乙酯MSDS
| 产品说明 | 乙酸乙酯(141-78-6)具有极性非质子传递溶剂,乙酸乙酯是EC3.4.19.3(焦谷氨酰肽酶I)抑制剂.乙酸乙酯溶解度,乙酸乙酯MSDS,乙酸乙酯结构式详见主页. |
| Introduction | 乙酸乙酯(141-78-6,Ethylacetate)is a polar aprotic solvent, an inhibitor of EC 3.4.19.3 (pyroglutamyl peptidase I), a metabolite and a metabolite of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
| Application1 | 乙酸乙酯可用于生化研究,蛋白质顺序分析。 |
| Application2 | 萃取剂,从水溶液中提取许多化合物(磷、钨、砷、钴),有机分析中用作结晶时的可以作为溶剂,分离糖类时作为校正温度计的标准物质,检定铋、金、铁、汞、氧化剂和铂,测定铋、硼、金、铁、钼、铂、钾和铊 |
| Application3 | 乙酸乙酯(141-78-6,Ethylacetate)有水果香,易挥发, 对空气敏感, 能吸水分,水分能使其缓慢分解而呈酸性反应,能与氯仿、醇、丙酮和醚混溶,溶于水(10%ml/ml),能溶解某些金属盐类(如氯化锂、氯化钴、氯化锌、氯化铁等,易燃,蒸气能与空气形成爆炸性混合物,半数致死量(大鼠,经口)11.10ml/kg,有刺激性, |
乙酸乙酯(141-78-6,Ethylacetate)药理学:
※乙酸乙酯(141-78-6,Ethylacetate)显示为透明无色液体,带有水果味。闪点24°F。不如水浓密。蒸气比空气重。 乙酸乙酯是乙酸和乙醇之间形成的乙酸酯。
※乙酸乙酯是具有极性非质子传递溶剂,是EC 3.4.19.3(焦谷氨酰肽酶I)抑制剂,代谢产物和酿酒酵母代谢产物的作用。它是乙酸酯,乙酯和挥发性有机化合物。 在酒精饮料中发现了乙酸乙酯。醋酸乙酯存在于谷物作物,萝卜,果汁,啤酒,葡萄酒,烈酒等中,由Anthemis nobilis(罗马洋甘菊)和悬钩子属植物生产。醋酸乙酯用于人造水果香精。乙酸乙酯在改性啤酒花提取物和脱咖啡因的茶或咖啡的生产中用作溶剂。也用于标记水果或蔬菜的颜色和油墨。在昆虫学领域,乙酸乙酯是用于昆虫收集和研究的有效窒息剂。在装有乙酸乙酯的杀灭缸中,蒸气会迅速杀死所收集的(通常是成年的)昆虫而不会对其造成破坏。因为它不吸湿,所以乙酸乙酯还可以使昆虫保持足够的柔软,以使其适合收集。
※乙酸乙酯是乙醚的一种有效替代溶剂,可在福尔马林-甲。醚沉降技术中用于粪便样品中卵,幼虫和囊肿的浓缩在嵌入的Ce掺杂的二氧化钛表面上的氧化铜存在下,乙醛是在乙醇和甲醛的氧化消耗过程中形成的反应中间体。
※乙酸乙酯是甲醛合成合成-苄基-大号-谷氨酸N-羧酸萘(BLG-NCA)的溶剂。
※Ethyl acetate, also known as 1-acetoxyethane or acetic ester, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as carboxylic acid esters. These are carboxylic acid derivatives in which the carbon atom from the carbonyl group is attached to an alkyl or an aryl moiety through an oxygen atom (forming an ester group). Ethyl acetate exists as a solid, soluble (in water), and an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). Ethyl acetate has been detected in multiple biofluids, such as saliva, feces, and urine. Within the cell, ethyl acetate is primarily located in the cytoplasm. Ethyl acetate exists in all eukaryotes, ranging from yeast to humans. Ethyl acetate is a sweet, anise, and balsam tasting compound that can be found in a number of food items such as loganberry, swede, ostrich fern, and acorn. This makes ethyl acetate a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products. Ethyl acetate has been linked to the inborn metabolic disorders including celiac disease.
乙酸乙酯(141-78-6,Ethylacetate)物理属性:
| 物理特性 | 值 | 单位 | 温度(摄氏度) | 资源 |
| Melting Point | -8.36E+01 | deg C | EXP | |
| Boiling Point | 77.1 | deg C | EXP | |
| log P (octanol-water) | 0.73 | (none) | EXP | |
| Water Solubility | 8.00E+04 | mg/L | 25 | EXP |
| Vapor Pressure | 93.2 | mm Hg | 25 | EXP |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.34E-04 | atm-m3/mole | 25 | EXP |
| Atmospheric OH Rate Constant | 1.60E-12 | cm3/molecule-sec | 25 | EXP |
| 警示图 | |
| 危险性 | warning |
| 危险性警示 | Not Available |
| 安全声明 | H225,H319,H336 |
| 安全防护 | P210,P261,P305+P351+P338 |
| 备注 | 避免吸入,误食以及与皮肤接触,危险:易燃,导致中枢神经系统损伤,肺及眼刺激, |
乙酸乙酯(141-78-6,Ethylacetate)危害标识:
| 象形图 |  |
| 信号 | Danger |
| GHS危险说明 | H225: Highly Flammable liquid and vapor [Danger Flammable liquids] |
| H319: Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] | |
| H336: May cause drowsiness or dizziness [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure; Narcotic effects] | |
| 防范说明代码 | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P280, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P337+P313, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, and P501 |
| (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| Perspectives for the microbial production of ethyl acetate Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2020 32656615 |
| Removal characteristics of mixed gas of ethyl acetate and 2-butanol by a biofilter packed with Jeju scoria Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering 2011 |
| Deceleration the hydrolysis reaction of ethyl acetate ester by β-cyclodextrin in basic medium: transition state analog Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry 2017 |
| Effect of ethyl acetate and trap colour on weevil captures in red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) pheromone traps International Journal of Tropical Insect Science 201 |
| Acidity function of methanesulfonic acid solutions in ethyl acetate Russian Chemical Bulletin 2001 |
乙酸乙酯(141-78-6,Ethylacetate)参考文献:
1、Perspectives for the microbial production of ethyl acetate Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2020 32656615
Shangjie Zhang, Feng Guo, Wei Yan, Weiliang Dong, Jie Zhou, Wenming Zhang, Fengxue Xin & Min Jiang
Abstract:Ethyl acetate is one of the short-chain esters and widely used in the food, beverage, and solvent areas. The ethyl acetate production currently proceeds through unsustainable and energy intensive processes, which are based on natural gas and crude oil. Microbial conversion of biomass-derived sugars into ethyl acetate may provide a sustainable alternative. In this review, the perspectives of bio-catalyzing ethanol and acetic acid to ethyl acetate using lipases in vitro was introduced. Besides, the crucial elements for high yield of ethyl acetate in fermentation was expounded. Also, metabolic engineering in yeasts to product ethyl acetate in vivo using alcohol acyl transferases (AAT) was discussed. Key points •The accumulation of acetyl-CoA is crucial for synthesizing ethyl acetate in vivo; AAT-mediated metabolic engineering could efficiently improve ethyl acetate production. Introduction Ethyl acetate is one of the short-chain esters, which is also known as a flavor compound. Ethyl acetate can be applied for the synthesis of biodiesels, paints, adhesives, herbicides, and resins (Alavijeh et al. 2015; Löser et al. 2014; Modi et al. 2007). Besides, it is also an environmentally friendly solvent due to its moderate polarity, non-toxicity, and biodegradability. The conventional industrial production of ethyl acetate was through Fisher esterification processes, in which ethanol and acetate were converted into ethyl acetate under high temperature (200–250 °C) with concentrated sulfuric acid as the catalyst (Löser et al. 2014). This process is highly energy-consuming and also causes severe corrosiveness and formation of a significant amount of hazardous wastes. Alternatively, biosynthesis of esters offers another promising alternative, which are usually carried out under mild conditions with high product yield and selectivity.
2、Removal characteristics of mixed gas of ethyl acetate and 2-butanol by a biofilter packed with Jeju scoria Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering 2011 桑圭锦,金钟K&李敏圭
Abstract:The removal characteristics of a mixed gas of ethyl acetate and 2-butanol by a biofilter packed with Jeju scoria were investigated. The experiments were conducted by changing the mixing ratio and the inlet loading rate of the mixed gas. There was no significant difference between the removal efficiency of ethyl acetate in the mixed gas and that of ethyl acetate in the single gas, while the removal efficiency of 2-butanol in the mixed gas was higher than that in the single gas. At the same loading rate, there was no significant difference between the removal capacity of ethyl acetate in the single gas and that in the mixed gas consisting of ethyl acetate at higher concentration than 2-butanol. However, the removal capacity of 2-butanol in the mixed gas was higher than that in the single gas when 2-butanol flowed through the biofilter at higher concentration than that of ethyl acetate.
3、Deceleration the hydrolysis reaction of ethyl acetate ester by β-cyclodextrin in basic medium: transition state analog Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry 2017
Sa’ib J. Khouri & Abdelmnim Altwaiq
Abstract Electrical conductivity measurements were used to study the hydrolysis reaction of dilute aqueous solution of ethyl acetate with the presence β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) within a concentration range between 0.00 and 0.00750 M in basic medium at 25.0 °C. 0.00265 M of β-CD was chosen as typical concentration for studying the same reaction at different temperatures between 21.0 and 35.0 °C. Two different values of activation energy for the hydrolysis reaction of free ethyl acetate and ethyl acetate/β-CD complex were evaluated, and their values are 46.3 and 62.0 kJ mol−1 respectively. The standard Gibbs energy of activation (?‡Go), standard enthalpy of activation (?‡Ho), and standard entropy of activation (?‡So) for the two different cases were evaluated. β-CD plays a notable role in retarding the rate of hydrolysis of ethyl acetate in basic medium.
4、Effect of ethyl acetate and trap colour on weevil captures in red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) pheromone traps International Journal of Tropical Insect Science 2013
Ahmad Hussen Al-Saoud (a1)
Abstract:Trapping of adult red palm weevil (RPW) Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Olivier using food-baited pheromone traps is a major component of the integrated pest management strategy currently adopted against the RPW in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Field trials were carried out in RPW-infested date plantations of Al-Rahba, Abu Dhabi, UAE from January to December 2010 to ascertain the combined influence of ethyl acetate (EA) and trap colours on weevil captures in RPW pheromone traps. Weevil captures were recorded throughout the experimental period with a sex ratio (male:female) of 1:2.2 and capture rates of 25.13 and 15.14 weevils/trap/month in traps with and without EA, respectively. Furthermore, treatments with black-coloured traps recorded significantly higher weevil captures.
5、Acidity function of methanesulfonic acid solutions in ethyl acetate Russian Chemical Bulletin 2001 I. S. Kislina & Sysoeva
Abstract:The acidity function of solutions of methanesulfonic acid (MSA) in ethyl acetate (EA) was measured by the indicator method at 25 °C in the 0.4—100% concentration range. Molecular complexes formed by MSA and EA show a higher ionizing activity than H5O2 + ions. The relative ionizing activity of the MSA·EA complexes and ion pairs formed by MSA and DMF was determined.
Ren 化学品安全技术说明书 | 版本:1.0 | |||
按照GB/T16483、GB/T17519编制 | 修订日期:10.07.2019 | |||
打印日期:19.02.2020 | ||||
版权所有:范德(北京)生物科技有限责任公司 | 最初编制日期:25.05.2017 | |||
公司网站:WWW.BIO-FOUNT.COM | SDS编号:BIOFOUNT-JT11988 | |||
版权所有:BIOFOUNT BEIJING BIO TECH CO.,LTD | 产品编号:JT11988 | |||
乙酸乙酯 | ||||
说明书目录 | ||||
第1部分 | 第2部分 | 危险性概述 | ||
第3部分 | 成分/组成信息 | 第4部分 | 急救措施 | |
第5部分 | 消防措施 | 第6部分 | 泄露应急处理 | |
第7部分 | 操作处置与储存 | 第8部分 | 接触控制/个体防护 | |
第9部分 | 理化性质 | 第10部分 | 稳定性和反应性 | |
第11部分 | 毒理学信息 | 第12部分 | 生态学危害信息 | |
第13部分 | 废弃处置 | 第14部分 | 运输信息 | |
第15部分 | 法律法规信息 | 第16部分 | 其他补充信息 | |
第1部分:化学品及企业标识 | ||||
1.1 产品标识 | ||||
乙酸乙酯 | ||||
ENGLISH NAME: | Ethylacetate | |||
JT11988 | ||||
BIOFOUNT | ||||
141-78-6 | ||||
1.2 安全技术说明书提供者的详情 | ||||
制造商或供应商名称: | ||||
制造地址: | 59 KANGTAI AVENUE BINHAI NEW DISTRICT TIANJIN 300450 TIANJIN CHINA 范德(天津)生物科技有限责任公司 天津市滨海新区康泰大道59号九州通绿谷健康产业园 邮政编码:300450 | |||
电话号码: | ||||
1.3 应急咨询电话 | ||||
紧急联系电话: | ||||
1.4 物质或混合物的推荐用途和限制用途 | ||||
已确认的各用途: | 仅用于科学研发,不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。 | |||
第2部分:危险性概述 | ||||
2.1 GHS危险性类别 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.2 GHS 标签要素,包括防范说明 | ||||
象形图 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
Danger | ||||
H225,H319,H336 | ||||
警告申明 | ||||
避免吸入,误食以及与皮肤接触 | ||||
P210,P261,P305+P351+P338 | ||||
事故响应 | ||||
1.化学品使用过程中,当出现事故或者有紧急情况发生时,当事人应第一时间向应急小组负责人汇报后,由应急小组采取措施防止事态扩大。2.应急小组对受害人采取救护措施。 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
废弃处置 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.3 物理和化学危险 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.4 健康危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.5 环境危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.6 其它危害物 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第3部分:成分/组成信息 | ||||
物质/混合物 | 暂无数据 | |||
3.1 物 质 | ||||
C4H8O2 | ||||
88.11 | ||||
110-91-8 | ||||
EC-编号 | 205-500-4 | |||
根据相应法规,无需披露具体组份。 | ||||
第4部分:急救措施 | ||||
4.1 必要的急救措施描述 | ||||
吸入 | ||||
立即将患者移至空气新鲜处,发现呼吸困难时,必须立即采取吸氧处理,停止呼吸时采取人工呼吸。同时联系及时就医。 | ||||
皮肤接触 | ||||
立即脱去或者剪去污染的衣物,迅速用大量的流动清水冲10-20分钟甚至更长时间后,赴医院就医。 | ||||
眼睛接触 | ||||
立即用大量的流动清水冲10-20分钟后赴医院就医处理。 | ||||
食入 | ||||
误食化学物品后,应立即采取措施进行催吐。1.若误食化学品呈酸性,则可服用大量牛奶和水,促使食如折呕吐。2.若误食化学品呈碱性,则可服用大量牛奶、清水和醋,促使其呕吐,紧急处理后,应及时送至医院进行治疗(仅供参考)。食如者昏迷状态下禁止催吐,以免造成窒息。 | ||||
4.2 最重要的症状和健康影响 | ||||
最重要的已知症状及作用已在标签(参见章节2.2)和/或章节11中介绍 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
4.4 对医生的特别提示 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第5部分:消防措施 | ||||
5.1 灭火介质 | ||||
采用泡沫灭火器、二氧化碳灭火器,避免造成二次污染发生。 | ||||
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
5.3 灭火注意事项及保护措施 | ||||
小规模着火需戴好口罩,防止有毒气体吸入。火灾发生时及时启动应急相应系统撤离至上风口处,并联系当地消防部门灭火。 | ||||
第6部分:泄露应急处理 | ||||
1.泄露后首先启动应急相应系统2.泄露处理前,需穿戴好安全安全防护鞋、穿戴好安全防护手套(强酸性物质需穿戴防酸碱手套)、根据吸入危险性穿戴相应防护面罩。 有关个人防护,请看第8部分。 | ||||
6.2 环境保护措施 | ||||
参照《范德生物化学废弃物处理方法》处理,防止对环境造成危害,处理后交由有资质的废弃物处理结构进行处理,以免造成环境污染。 | ||||
参照《范德生物化学品废弃物处理方法》对泄露的化学品进行处理,处理前需用化学品吸附岩棉对泄露区域进行围挡,形成“围堰”防止泄露扩大。 | ||||
6.4 参考其他部分 | ||||
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。 | ||||
第7部分:操作处置与储存 | ||||
7.1 安全操作的注意事项 | ||||
使用过程请穿戴好口罩,手套等防护用品,避免与皮肤接触、吸入、误食危险。 有关预防措施,请参见章节2.2。 | ||||
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性 | ||||
暂时无法提供详细数据,尽可能避免与其他化合物混合存储,避光、通风处存储。 | ||||
第8部分:接触控制/个体防护 | ||||
8.1 控制参数 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
8.2 暴露控制 | ||||
适当的技术控制 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
个体防护装备 | ||||
一般情况下穿戴安全防护眼镜即可,如有飞溅液体、粉末产生时,请佩戴防溅面罩进行防护。穿戴的防护用品需取得如:GB、NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 等相关认证。 | ||||
手套脱去注意事项:手套在使用前必须进行检查,请使用正确的方法脱除手套(不接触手套外部表面),避免身体任何皮肤部位接触到此产品。根据相关法律法规和实验室管理规范制度,手套使用过后,请将被污染的手套谨慎处理,工作后清洗并吹干双手。 所选择的保护手套必须符合法规《劳动防护用品配备标准》、(EU)2016/425以及从此类法规衍生出来的EN 374标准规范。 完全接触保护要求: 手套材料:丁腈橡胶 手套最小的层厚度:0.11 MM 手套溶剂渗透时间:480 分钟 飞溅保护要求: 材料:丁腈橡胶 最小的层厚度 0.11 MM 溶剂渗透时间:480 分钟 如果以溶剂形式应用或与其它物质混合应用,或在不同于《劳动防护用品配备标准》,EN 374规定的条件下应用,请与EC批准的手套的供应商联系。该条只是作为推荐性建议,如遇特殊情况,务必请熟悉该产品属性的专家,选取相关防护用品。此条建议不应该被认定为适应所有特殊条件防护,请根据所处工作条件请求专业工程师指导采取相应防护措施。 | ||||
选择身体部分的防护措施,需要根据危险物质的类型、浓度、量以及特定的工作环境。身体部分防护设备、防护服的类型,必须根据使用者工作场所中的危险物质的浓度、数量进行选择。 | ||||
一般情况下穿戴普通的医用口罩保护呼吸系统即可。有酸雾产生式活性炭类口罩起不到防护作用,如需对粉尘造成损害进行防护时,请采用N95型(US)或P1型(EN 143)类口罩或者防尘面具。特殊情况下使用自吸式呼吸器时,使用的呼吸器必须对呼吸器密闭性、空气供应系统、供气压进行测试,当然呼吸器需通过强制认证标准如:GB、NIOSH(US)、CEN(EU)。 | ||||
环境暴露的控制 | ||||
不要让产品进入下水道。 | ||||
第9部分:理化特性 | ||||
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息 | ||||
形状:暂无数据 | ||||
颜色:暂无数据 | ||||
气味 | 暂无数据 | |||
气味阈值 | 暂无数据 | |||
暂无数据 | ||||
-83°C | ||||
初沸点和沸程 | 77°C | |||
闪点 | -3 °C | |||
蒸发速率 | 暂无数据 | |||
易燃性(固体,气体) | 暂无数据 | |||
高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 | 暂无数据 | |||
蒸气压 | 111.7±0.1 mmHg at 25°C | |||
蒸气焓 | 31.9±0.0 kJ/mol | |||
密度/相对密度 | 0.9020 | |||
10.0 g/100g in waterWikidataQ40715387.8-88.0 g/kg in waterWikidataQ40715387.9 g/kg in waterWikidataQ4071539-11 g/100g in waterWikidataQ407153 | ||||
正辛醇/水分配系数 | Log Kow (KOWWIN v1.67 estimate) = 0.86
Log Kow (Exper. database match) = 0.73
Exper. Ref: Hansch,C et al. (1995)/ Boiling Pt, Melting Pt, Vapor Pressure Estimations (MPBPWIN v1.42):
Boiling Pt (deg C): 77.91 (Adapted Stein & Brown method)
Melting Pt (deg C): -82.08 (Mean or Weighted MP)
VP(mm Hg,25 deg C): 98.3 (Mean VP of Antoine & Grain methods)
MP (exp database): -83.6 deg C
BP (exp database): 77.1 deg C
VP (exp database): 9.32E+01 mm Hg at 25 deg C | |||
正辛醇空气分配系数 | Log Kow used: 0.73 (exp database)
Log Kaw used: -2.261 (exp database)
Log Koa (KOAWIN v1.10 estimate): 2.991
Log Koa (experimental database): 2.700 | |||
自燃温度 | 暂无数据 | |||
分解温度 | 暂无数据 | |||
黏度 | 暂无数据 | |||
暂无数据 | ||||
氧化性 | 暂无数据 | |||
根据碎片估算水溶胶 | Wat Sol (v1.01 est) = 38942 mg/L
Wat Sol (Exper. database match) = 80000.00
Exper. Ref: BANERJEE,S (1984) | |||
亨利定律常数(25摄氏度) | Bond Method : 2.33E-004 atm-m3/mole
Group Method: 1.58E-004 atm-m3/mole
Exper Database: 1.34E-04 atm-m3/mole
Henrys LC [VP/WSol estimate using EPI values]: 3.808E-004 atm-m3 | |||
9.2 其他安全信息 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第10部分:稳定性和反应性 | ||||
10.1 稳定性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.2 危险反应 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.3 应避免的条件 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.4 禁配物 | ||||
强氧化剂 | ||||
10.5 危险的分解产物 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第11部分:毒理学信息 | ||||
11.1 毒理学影响信息 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
呼吸或皮肤过敏 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
生殖毒性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触) | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
吸入危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
附加说明 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第12部分:生态学危害信息 | ||||
12.1 生态毒性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.2 持久性和降解性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.3 快速生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin1 (Linear Model) : 0.8798
Biowin2 (Non-Linear Model) : 0.9971 | ||||
12.4 专家调查生物降解结果 | ||||
Biowin3 (Ultimate Survey Model): 3.1447 (weeks )
Biowin4 (Primary Survey Model) : 3.9496 (days ) | ||||
12.5 MITI生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin5 (MITI Linear Model) : 0.8440
Biowin6 (MITI Non-Linear Model): 0.9477 | ||||
12.6 厌氧生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin7 (Anaerobic Linear Model): 0.8748 | ||||
12.7 现成的生物降解性预测 | ||||
YES | ||||
12.8 碳氢化合物生物降解 | ||||
Structure incompatible with current estimation method! | ||||
12.9 对气溶胶的吸附 | ||||
Vapor pressure (liquid/subcooled): 1.24E+004 Pa (93.2 mm Hg)
Log Koa (Exp database): 2.700
Kp (particle/gas partition coef. (m3/ug)):
Mackay model : 2.41E-010
Octanol/air (Koa) model: 1.23E-010 | ||||
12.10 羟基自由基反应 | ||||
OVERALL OH Rate Constant = 1.7038 E-12 cm3/molecule-sec
Half-Life = 6.278 Days (12-hr day; 1.5E6 OH/cm3)
Half-Life = 75.331 Hrs | ||||
12.11 臭氧反应 | ||||
No Ozone Reaction Estimation | ||||
12.12 空气中颗粒物吸附的分数(PHI) | ||||
1.4E-008 (Junge,Mackay)
Note: the sorbed fraction may be resistant to atmospheric oxidation | ||||
12.13 土壤吸附系数 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.14 碱/酸催化水解(25℃) | ||||
Koc : 6.131
Log Koc: 0.788 / Aqueous Base/Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis (25 deg C) [HYDROWIN v1.67]:
Total Kb for pH > 8 at 25 deg C : 1.208E-001 L/mol-sec
Kb Half-Life at pH 8: 66.387 days
Kb Half-Life at pH 7: 1.818 years / | ||||
12.15 利用对数KOW估算生物累积量 | ||||
Log BCF from regression-based method = 0.500 (BCF = 3.162)
log Kow used: 0.73 (expkow database) | ||||
12.16 废水处理中的去除 | ||||
Total removal: 8.07 percent
Total biodegradation: 0.09 percent
Total sludge adsorption: 1.68 percent
Total to Air: 6.30 percent
(using 10000 hr Bio P,A,S) | ||||
12.17 三级逸度模型 | ||||
Mass Amount Half-Life Emissions
(percent) (hr) (kg/hr)
Air 16.3 160 1000
Water 43.7 360 1000
Soil 39.9 720 1000
Sediment 0.0841 3.24e+003 0
Persistence Time: 250 hr | ||||
12.18 土壤中的迁移性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.19 PBT和VPVB的结果评价 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.20 其他环境有害作用 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第13部分:废弃处置 | ||||
13.1 废物处理 | ||||
None | ||||
None | ||||
第14部分:运输信息 | ||||
14.1 联合国编号 / UN NUMBER | ||||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID: | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IMDG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
14.2 联合国运输名称 / UN PROPER SHIPPING NAME | ||||
欧洲陆运危规: | None | |||
国际海运危规: | None | |||
国际空运危规: | None | |||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID: | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IMDG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID : | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IM0DG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
None | ||||
14.6 特殊防范措施 / SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR USER | ||||
None | ||||
None | ||||
第15部分:法律法规信息 | ||||
适用法规 | ||||
《中华人民共和国安全生产法》、《职业病防治法》、《化学化工实验室安全管理规范》 | ||||
其它的规定 | ||||
《生产安全事故报告和调查处理条例》、《职业病防治法》、《职业安全和卫生法》美国1970 | ||||
第16部分:其他补充信息 | ||||
其他信息 版权所有:BIOFOUNT BEIJING BIO TECH CO.,LTD 公司。许可无限制纸张拷贝,仅限于内部使用。 上述信息视为正确,但不包含所有的信息,仅作为指引使用。本文件中的信息是基于我们目前所知,就正确的安全提示来说适用于本品。该信息不代表对此产品性质的保证。BIOFOUNT公司及其附属公司对任何操作或者接触上述产品而引起的损害不负有任何责任。更多使用条款,参见发票或包装条的反面。 更多销售条款及条件请参见HTTP://WWW.BIO-FOUNT.COM/或发票或装箱单的背面。欲悉详情,请联系:SALES@BIO-FOUNT.COM | ||||
- 相关产品
-
< >
- 推荐产品
-
< >
- 最新产品
-
< >
新闻
怎么做细胞爬片免疫组化染色实验
细胞爬片免疫组化染色,是通过细胞爬片是让玻片浸在细胞培养基内,细胞在玻片上生长,主要用于组织学,免疫组织化学...
2020/7/20 22:04:33
提取病毒RNA的实验方法
提取病毒RNA方法分别有:异硫氰酸胍的提取病毒RNA方法、TRIzol LS提取法、Trizol法提取法等等...
2020/7/22 20:29:26
各种微流控芯片键合方法的优缺点
微流控芯片键合:目前主要有激光焊接、热压键合、胶键合、超音波焊接,每种方法都有各自的优缺点。本文主要介绍聚酯...
2023/7/28 10:43:09

新一代微流控键合解决方案
微流控键合解决方案:微流控芯片制造的一个重要环节,也是最容易被忽视的--芯片键合。其中一个重要因素是:微流控...
2023/7/27 12:44:28
荧光素钾盐使用说明
D-荧光素钾盐(K+)设计用于体外和体内生物发光测定。D-荧光素的质量和纯度对于获得良好和可重复的结果至关重...
2023/7/20 11:05:11
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白)
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白):牛血清白蛋白(BSA)有多种形式,如何选择适合自己的牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是一...
2023/2/14 13:09:18

牛血清白蛋白(BSA)常见问题
牛血清白蛋白(BSA)常见问题:牛血清白蛋白(BSA)在实验室中是通用的,可用于蛋白质印迹、细胞组织培养、P...
2022/10/19 9:39:51
pubmed使用方法(技巧)
pubmed使用方法(技巧):PubMed是一个关于医学问题的学术文章和书籍的数据库。因为它是一份学术期刊,...
2022/10/18 18:06:07
BSA(牛血清白蛋白)
BSA(牛血清白蛋白):牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是一种球状蛋白质,牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是发现于牛血浆中的主要...
2022/10/18 16:48:12
冻干培养细菌的方法
冻干培养细菌的方法:冷冻干燥,也称为冻干或冷冻干燥,是在产品冷冻后除去水分并将其置于真空中的过程。这使得冰可...
2022/10/16 8:27:31




 购物车
购物车 



