-
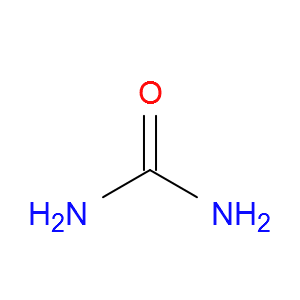
尿素
NMR and HPLC COA下载 MSDS下载 - Names:
Urea
- CAS号:
57-13-6
MDL Number: MFCD00008022 - MF(分子式): CH4N2O MW(分子量): 60.06
- EINECS:200-315-5 Reaxys Number:
- Pubchem ID:24858038 Brand:BIOFOUNT
| 货品编码 | 规格 | 纯度 | 价格 (¥) | 现价(¥) | 特价(¥) | 库存描述 | 数量 | 总计 (¥) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JY0003-500g | 500g | AR,99% | ¥ 58.00 | ¥ 58.00 | Instock | ¥ 0.00 |
| 中文别名 | 尿素(57-13-6);脲; 碳酰二胺脲; 尿素,碳酰胺; 碳酰胺; 碳酰二胺; 胺甲醯胺; 涂硫尿素 |
| 英文别名 | Urea(57-13-6);Urea Carbamide;Carbonyl diamide;carbonyl diamine;carbonyldiamide |
| CAS号 | 57-13-6 |
| SMILES | C(=N)(N)O |
| Inchi | InChI=1S/CH4N2O/c2-1(3)4/h(H4,2,3,4) |
| InchiKey | XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| 分子式 Formula | CH4N2O |
| 分子量 Molecular Weight | 60.06 |
| 闪点 FP | 53.7±22.6 °C |
| 熔点 Melting point | 132.7°C |
| 沸点 Boiling point | 165.1±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Polarizability极化度 | 4.7±0.5 10-24cm3 |
| 密度 Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
| 蒸汽压 Vapor Pressure | 0.6±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| 溶解度Solubility | 溶于水、甲醇、乙醇,微溶于乙醚、氯仿、苯。 |
| 性状 | white crystalline powder |
| 储藏条件 Storage conditions | 密封保存。 |
尿素(Urea;57-13-6)毒理性质:
| 动物 | 测试类型 | 途径 | 实验摄入量 (标准摄入量) | 影响 | 文献来源 |
| dog | LDLo | intravenous | 3gm/kg (3000mg/kg) | "Abdernalden's Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden." Vol. 4, Pg. 1353, 1935. | |
| dog | LDLo | subcutaneous | 3gm/kg (3000mg/kg) | "Abdernalden's Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden." Vol. 4, Pg. 1353, 1935. | |
| domestic animals - goat/sheep | LDLo | oral | 511mg/kg (511mg/kg) | LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: DYSPNEA GASTROINTESTINAL: CHANGES IN STRUCTURE OR FUNCTION OF SALIVARY GLANDS BEHAVIORAL: TETANY |
American Journal of Physiology. Vol. 153, Pg. 41, 1948. |
| frog | LDLo | subcutaneous | 600mg/kg (600mg/kg) | "Abdernalden's Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden." Vol. 4, Pg. 1353, 1935. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intravenous | 4600mg/kg (4600mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: ANTIPSYCHOTIC BEHAVIORAL: CHANGES IN MOTOR ACTIVITY (SPECIFIC ASSAY) BEHAVIORAL: ALTERED SLEEP TIME (INCLUDING CHANGE IN RIGHTING REFLEX) |
Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 13, Pg. 749, 1977. |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 11gm/kg (11000mg/kg) | Gigiena Truda i Professional'nye Zabolevaniya. Labor Hygiene and Occupational Diseases. Vol. 31(12), Pg. 53, 1987. | |
| mouse | LD50 | subcutaneous | 9200mg/kg (9200mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: CHANGES IN MOTOR ACTIVITY (SPECIFIC ASSAY) BEHAVIORAL: ANTIPSYCHOTIC BEHAVIORAL: ALTERED SLEEP TIME (INCLUDING CHANGE IN RIGHTING REFLEX) |
Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 13, Pg. 749, 1977. |
| mouse | LDLo | intraperitoneal | 6608mg/kg (6608mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: COMA BEHAVIORAL: CONVULSIONS OR EFFECT ON SEIZURE THRESHOLD |
Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. Vol. 57, Pg. 19, 1936. |
| pigeon | LDLo | subcutaneous | 14800mg/kg (14800mg/kg) | "Ueber die Wirkung Verschiedener Gifte Auf Vogel, Dissertation," Forchheimer, L., Pharmakologischen Institut der Universitat Wurzburg, Fed. Rep. Ger., 1931Vol. -, Pg. -, 1931. | |
| rabbit | LDLo | intravenous | 4800mg/kg (4800mg/kg) | "Abdernalden's Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden." Vol. 4, Pg. 1353, 1935. | |
| rabbit | LDLo | oral | 10gm/kg (10000mg/kg) | BLOOD: HEMORRHAGE LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: STRUCTURAL OR FUNCTIONAL CHANGE IN TRACHEA OR BRONCHI BRAIN AND COVERINGS: OTHER DEGENERATIVE CHANGES |
Japanese Journal of Veterinary Science. Vol. 15, Pg. 125, 1953. |
| rabbit | LDLo | subcutaneous | 3gm/kg (3000mg/kg) | "Abdernalden's Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden." Vol. 4, Pg. 1353, 1935. | |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal | > 5gm/kg (5000mg/kg) | Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archiv fuer Pharmakologie und Experimentelle Pathologie. Vol. 257, Pg. 296, 1967. | |
| rat | LD50 | intratracheal | 567mg/kg (567mg/kg) | LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: DYSPNEA BLOOD: METHEMOGLOBINEMIA-CARBOXYHEMOGLOBIN BEHAVIORAL: CONVULSIONS OR EFFECT ON SEIZURE THRESHOLD |
Gigiena Truda i Professional'nye Zabolevaniya. Labor Hygiene and Occupational Diseases. Vol. 30(3), Pg. 43, 1986. |
| rat | LD50 | intravenous | 5300mg/kg (5300mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: ALTERED SLEEP TIME (INCLUDING CHANGE IN RIGHTING REFLEX) BEHAVIORAL: CHANGES IN MOTOR ACTIVITY (SPECIFIC ASSAY) BEHAVIORAL: ANTIPSYCHOTIC |
Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 13, Pg. 749, 1977. |
| rat | LD50 | oral | 8471mg/kg (8471mg/kg) | Gigiena i Sanitariya. For English translation, see HYSAAV. Vol. 51(6), Pg. 8, 1986. | |
| rat | LD50 | subcutaneous | 8200mg/kg (8200mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: CHANGES IN MOTOR ACTIVITY (SPECIFIC ASSAY) BEHAVIORAL: ANTIPSYCHOTIC BEHAVIORAL: ALTERED SLEEP TIME (INCLUDING CHANGE IN RIGHTING REFLEX) |
Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 13, Pg. 749, 1977. |
尿素(Urea;57-13-6)物理性质:
| Physical Property | Value | Units | Temp (deg C) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 132.7 | deg C | EXP | |
| pKa Dissociation Constant | 0.1 | (none) | 21 | EXP |
| log P (octanol-water) | -2.11E+00 | (none) | EXP | |
| Water Solubility | 5.45E+05 | mg/L | 25 | EXP |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.74E-12 | atm-m3/mole | 25 | EST |
| Atmospheric OH Rate Constant | 4.00E-11 | cm3/molecule-sec | 25 | EST |
尿素(CAS:57-13-6;英文名:Urea Standard Solution (calculated as N)实验注意事项:
1.使用57-13-6实验前需戴好防护眼镜,穿戴防护服和口罩,佩戴手套,避免与皮肤接触。
2.使用57-13-6实验过程中如遇到有毒或者刺激性物质及有害物质产生,必要时实验操作需要手套箱内完成以免对实验人员造成伤害。
3.取样品57-13-6的移液枪头需及时更换,必要时为避免交叉污染尽可能选择滤芯吸头。
4.称量药品时选用称量纸,并无风处取药和称量以免扬撒,试剂的容器使用前务必确保干净,并消毒。
5.取药品57-13-6时尽量采用多个药勺分别使用,使用后清洗干净。
6.实验后产生的废弃物需分类存储,并交于专业生物废气物处理公司处理,以免造成环境污染。
大规格定制:定制产品请将信息发送至sales@bio-fount.com。
Experimental considerations:
1. Wear protective glasses, protective clothing and masks, gloves, and avoid contact with the skin during the experiment.
2. The waste generated after the experiment needs to be stored separately, and handed over to a professional biological waste gas treatment company to avoid environmental pollution.
Tag:尿素蒸汽压,尿素合成,尿素标准,尿素应用,尿素合成,尿素沸点,尿素闪点,尿素用途,尿素溶解度,尿素价格,尿素作用,尿素结构式,尿素用处
| 产品说明 | 尿素(57-13-6)有氨的气味和咸味,加热温度高于其熔点时则分解成缩二脲,氨和三聚氰酸.尿素溶解度,尿素MSDS,尿素结构式详见主页. |
| Introduction | Urea appears as solid odorless white crystals or pellets. Density 1.335 g /cc. Noncombustible. |
| Application1 | 尿素是具有两个C-结合的胺基的羰基。 它具有面粉处理剂,人类代谢物,大型蚤(Daphnia magna)代谢物,酿酒酵母(Saccharomyces cerevisiae)代谢物,大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)代谢物,小鼠代谢物和肥料的作用。 |
| Application2 | 校准仪器和装置;评价方法;工作标准;质量保证/质量控制 |
| Application3 | Urea is a monocarboxylic acid amide and a one-carbon compound. It derives from a carbonic acid. It is a tautomer of a carbamimidic acid. |
| 警示图 | |
| 危险性 | warning |
| 危险性警示 | Not Available |
| 安全声明 | H316 ,H320 |
| 安全防护 | P264,P305+P351+P338,P332+P313,P337+P313 |
| 备注 | 避免吸入,误食以及与皮肤接触 |
| Ryo Yoshida, Haruhiko Katoh, Seizo Sumida, Ichiki Takemoto, Junya Takahashi, Katsuzo Kamoshita, "Urea derivatives, and their production and use." U.S. Patent US4334912, issued 0000. |
| Leuthardt, F.; Glasson, B. Biological synthesis of urea. Verhandl. Ver. schweiz. Physiol. (1942), 21 25-7. |
| Leuthardt, F.; Glasson, B. Biological synthesis of urea. Verhandl. Ver. schweiz. Physiol. (1942), 21 25-7. |
| Kobayashi N, Katsumata H, Uto Y, Goto J, Niwa T, Kobayashi K, Mizuuchi Y: A monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of glycolithocholic acid sulfate in human urine for liver functi |
| Somogyi A, Siebert D, Bochner F: Determination of endogenous concentrations of N1-methylnicotinamide in human plasma and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1990 May 15;187( |
Abstract:The purpose of the present study was to determine the diagnostic accuracy of vaginal urea and creatinine levels in the detection of premature rupture of membrane (PROM). The Cochrane (central), EMBASE, PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science were searched for studies published from the inception of the databases up to January 2020. We included published observational full-text articles. The mean differences (MD) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were calculated. The significance level was set as 0.05. Eleven studies (n = 1324) were considered for meta-analysis. Using the bivariate model, the summary estimate of sensitivity and specificity for urea was 0.96 (95% CI: 0.86, 0.98) and 0.93 (95% CI: 0.83, 0.97), respectively. The summary estimate of sensitivity and specificity for creatinine was 0.98 (95% CI: 0.92, 0.99) and 0.97 (95% CI: 0.89, 0.99), respectively. The overall mean of urea and creatinine in the case group was significantly higher than that in the control group (MD = 12.63, 95%, CI [12.01, 13.25]) and (MD = 0.31, 95%, CI [0.29, 0.32]), respectively. The results of this systematic review showed that the mean of urea and creatinine in the case group was significantly higher than that in the control group and the sensitivity and specificity of creatinine is higher than urea in the diagnosis of PROM.
2.Age, Pulse, Urea and Albumin (APUA) Model: A Tool for Predicting in-Hospital Mortality of Community-Acquired Pneumonia Adapted for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes/PMID 33116713; Diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity : targets and therapy 2020; 13(?):3617-3626/Name matches: albumin urea
Abstract:
Objective: The aim of this study was to develop a tool for predicting in-hospital mortality of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM).
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on 531 CAP patients with T2DM at The First Hospital of Qinhuangdao. The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality. Variables to develop the nomogram were selected using multiple logistic regression analysis. Discrimination was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Calibration was evaluated using the Hosmer-Lemeshow test and calibration plot.
Results: Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that age, pulse, urea and albumin (APUA) were independent risk predictors. Based on these results, we developed a nomogram (APUA model) for predicting in-hospital mortality of CAP in T2DM patients. In the training set, the area under the curve (AUC) of the APUA model was 0.814 (95% CI: 0.770-0.853), which was higher than the AUCs of albumin alone, CURB-65 and Pneumonia Severity Index (PSI) class (p<0.05). The Hosmer-Lemeshow test (χ 2=5.298, p=0.808) and calibration plot (p=0.802) showed excellent agreement between the predicted possibility and the actual observation in the APUA model. The results of the validation set were similar to those of the training set.
Conclusion: The APUA model is a simple and accurate tool for predicting in-hospital mortality of CAP, adapted for patients with T2DM. The predictive performance of the APUA model was better than CURB-65 and PSI class.
Keywords: albumin; community-acquired pneumonia; mortality; type 2 diabetes.
3.Delayed urea differential enhancement CEST (dudeCEST)-MRI with T 1 correction for monitoring renal urea handling/PMID: 33180343 DOI: 10.1002/mrm.28583
Abstract:
Purpose: We demonstrate a method of delayed urea differential enhancement CEST for probing urea recycling action of the kidney using expanded multi-pool Lorentzian fitting and apparent exchange-dependent relaxation compensation.
Methods: T1 correction of urea CEST contrast by apparent exchange-dependent relaxation was tested in phantoms. Nine mice were scanned at 7 Tesla following intraperitoneal injection of 2M 150 μL urea, and later saline. T1 maps and Z-spectra were acquired before and 20 and 40 min postinjection. Z-spectra were fit to a 7-pool Lorentzian model for CEST quantification and compared to urea assay of kidney homogenate. Renal injury was induced by aristolochic acid in 7 mice, and the same scan protocol was performed.
Results: Apparent exchange-dependent relaxation corrected for variable T1 times in phantoms. Urea CEST contrast at +1 ppm increased significantly at both time points following urea injection in the inner medulla and papilla. When normalizing the postinjection urea CEST contrast to the corresponding baseline value, both urea and saline injection resulted in identical fold changes in urea CEST contrast. Urea assay of kidney homogenate showed a significant correlation to both apparent exchange-dependent relaxation (R2 = 0.4687, P = .0017) and non-T1 -corrected Lorentzian amplitudes (R2 = 0.4964, P = .0011). Renal injury resulted in increased T1 time in the cortex and reduced CEST contrast change upon urea and saline infusion.
Conclusion: Delayed urea enhancement following infusion can provide insight into renal urea handling. In addition, changes in CEST contrast at 1.0 ppm following saline infusion may provide insight into renal function.
Keywords: AREX; CEST; MRI; kidney; urea.
Ren 化学品安全技术说明书 | 版本:1.0 | |||
按照GB/T16483、GB/T17519编制 | 修订日期:10.07.2019 | |||
打印日期:19.02.2020 | ||||
版权所有:范德(北京)生物科技有限责任公司 | 最初编制日期:25.05.2017 | |||
公司网站:WWW.BIO-FOUNT.COM | SDS编号:BIOFOUNT-JY0003 | |||
版权所有:BIOFOUNT BEIJING BIO TECH CO.,LTD | 产品编号:JY0003 | |||
尿素 | ||||
说明书目录 | ||||
第1部分 | 第2部分 | 危险性概述 | ||
第3部分 | 成分/组成信息 | 第4部分 | 急救措施 | |
第5部分 | 消防措施 | 第6部分 | 泄露应急处理 | |
第7部分 | 操作处置与储存 | 第8部分 | 接触控制/个体防护 | |
第9部分 | 理化性质 | 第10部分 | 稳定性和反应性 | |
第11部分 | 毒理学信息 | 第12部分 | 生态学危害信息 | |
第13部分 | 废弃处置 | 第14部分 | 运输信息 | |
第15部分 | 法律法规信息 | 第16部分 | 其他补充信息 | |
第1部分:化学品及企业标识 | ||||
1.1 产品标识 | ||||
尿素 | ||||
ENGLISH NAME: | Urea Standard Solution (calculated as N) | |||
JY0003 | ||||
BIOFOUNT | ||||
57-13-6 | ||||
1.2 安全技术说明书提供者的详情 | ||||
制造商或供应商名称: | ||||
制造地址: | 59 KANGTAI AVENUE BINHAI NEW DISTRICT TIANJIN 300450 TIANJIN CHINA 范德(天津)生物科技有限责任公司 天津市滨海新区康泰大道59号九州通绿谷健康产业园 邮政编码:300450 | |||
电话号码: | ||||
1.3 应急咨询电话 | ||||
紧急联系电话: | ||||
1.4 物质或混合物的推荐用途和限制用途 | ||||
已确认的各用途: | 仅用于科学研发,不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。 | |||
第2部分:危险性概述 | ||||
2.1 GHS危险性类别 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.2 GHS 标签要素,包括防范说明 | ||||
象形图 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
Warning | ||||
H316 ,H320 | ||||
警告申明 | ||||
避免吸入,误食以及与皮肤接触 | ||||
P264,P305+P351+P338,P332+P313,P337+P313 | ||||
事故响应 | ||||
1.化学品使用过程中,当出现事故或者有紧急情况发生时,当事人应第一时间向应急小组负责人汇报后,由应急小组采取措施防止事态扩大。2.应急小组对受害人采取救护措施。 | ||||
密封保存。 | ||||
废弃处置 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.3 物理和化学危险 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.4 健康危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.5 环境危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.6 其它危害物 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第3部分:成分/组成信息 | ||||
物质/混合物 | 暂无数据 | |||
3.1 物 质 | ||||
CH4N2O | ||||
60.06 | ||||
110-91-8 | ||||
EC-编号 | 200-315-5 | |||
根据相应法规,无需披露具体组份。 | ||||
第4部分:急救措施 | ||||
4.1 必要的急救措施描述 | ||||
吸入 | ||||
立即将患者移至空气新鲜处,发现呼吸困难时,必须立即采取吸氧处理,停止呼吸时采取人工呼吸。同时联系及时就医。 | ||||
皮肤接触 | ||||
立即脱去或者剪去污染的衣物,迅速用大量的流动清水冲10-20分钟甚至更长时间后,赴医院就医。 | ||||
眼睛接触 | ||||
立即用大量的流动清水冲10-20分钟后赴医院就医处理。 | ||||
食入 | ||||
误食化学物品后,应立即采取措施进行催吐。1.若误食化学品呈酸性,则可服用大量牛奶和水,促使食如折呕吐。2.若误食化学品呈碱性,则可服用大量牛奶、清水和醋,促使其呕吐,紧急处理后,应及时送至医院进行治疗(仅供参考)。食如者昏迷状态下禁止催吐,以免造成窒息。 | ||||
4.2 最重要的症状和健康影响 | ||||
最重要的已知症状及作用已在标签(参见章节2.2)和/或章节11中介绍 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
4.4 对医生的特别提示 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第5部分:消防措施 | ||||
5.1 灭火介质 | ||||
采用泡沫灭火器、二氧化碳灭火器,避免造成二次污染发生。 | ||||
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
5.3 灭火注意事项及保护措施 | ||||
小规模着火需戴好口罩,防止有毒气体吸入。火灾发生时及时启动应急相应系统撤离至上风口处,并联系当地消防部门灭火。 | ||||
第6部分:泄露应急处理 | ||||
1.泄露后首先启动应急相应系统2.泄露处理前,需穿戴好安全安全防护鞋、穿戴好安全防护手套(强酸性物质需穿戴防酸碱手套)、根据吸入危险性穿戴相应防护面罩。 有关个人防护,请看第8部分。 | ||||
6.2 环境保护措施 | ||||
参照《范德生物化学废弃物处理方法》处理,防止对环境造成危害,处理后交由有资质的废弃物处理结构进行处理,以免造成环境污染。 | ||||
参照《范德生物化学品废弃物处理方法》对泄露的化学品进行处理,处理前需用化学品吸附岩棉对泄露区域进行围挡,形成“围堰”防止泄露扩大。 | ||||
6.4 参考其他部分 | ||||
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。 | ||||
第7部分:操作处置与储存 | ||||
7.1 安全操作的注意事项 | ||||
使用过程请穿戴好口罩,手套等防护用品,避免与皮肤接触、吸入、误食危险。 有关预防措施,请参见章节2.2。 | ||||
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性 | ||||
暂时无法提供详细数据,尽可能避免与其他化合物混合存储,避光、通风处存储。 | ||||
第8部分:接触控制/个体防护 | ||||
8.1 控制参数 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
8.2 暴露控制 | ||||
适当的技术控制 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
个体防护装备 | ||||
一般情况下穿戴安全防护眼镜即可,如有飞溅液体、粉末产生时,请佩戴防溅面罩进行防护。穿戴的防护用品需取得如:GB、NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 等相关认证。 | ||||
手套脱去注意事项:手套在使用前必须进行检查,请使用正确的方法脱除手套(不接触手套外部表面),避免身体任何皮肤部位接触到此产品。根据相关法律法规和实验室管理规范制度,手套使用过后,请将被污染的手套谨慎处理,工作后清洗并吹干双手。 所选择的保护手套必须符合法规《劳动防护用品配备标准》、(EU)2016/425以及从此类法规衍生出来的EN 374标准规范。 完全接触保护要求: 手套材料:丁腈橡胶 手套最小的层厚度:0.11 MM 手套溶剂渗透时间:480 分钟 飞溅保护要求: 材料:丁腈橡胶 最小的层厚度 0.11 MM 溶剂渗透时间:480 分钟 如果以溶剂形式应用或与其它物质混合应用,或在不同于《劳动防护用品配备标准》,EN 374规定的条件下应用,请与EC批准的手套的供应商联系。该条只是作为推荐性建议,如遇特殊情况,务必请熟悉该产品属性的专家,选取相关防护用品。此条建议不应该被认定为适应所有特殊条件防护,请根据所处工作条件请求专业工程师指导采取相应防护措施。 | ||||
选择身体部分的防护措施,需要根据危险物质的类型、浓度、量以及特定的工作环境。身体部分防护设备、防护服的类型,必须根据使用者工作场所中的危险物质的浓度、数量进行选择。 | ||||
一般情况下穿戴普通的医用口罩保护呼吸系统即可。有酸雾产生式活性炭类口罩起不到防护作用,如需对粉尘造成损害进行防护时,请采用N95型(US)或P1型(EN 143)类口罩或者防尘面具。特殊情况下使用自吸式呼吸器时,使用的呼吸器必须对呼吸器密闭性、空气供应系统、供气压进行测试,当然呼吸器需通过强制认证标准如:GB、NIOSH(US)、CEN(EU)。 | ||||
环境暴露的控制 | ||||
不要让产品进入下水道。 | ||||
第9部分:理化特性 | ||||
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息 | ||||
形状:暂无数据 | ||||
颜色:暂无数据 | ||||
气味 | 暂无数据 | |||
气味阈值 | 暂无数据 | |||
暂无数据 | ||||
132.7°C | ||||
初沸点和沸程 | 165.1±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |||
闪点 | 53.7±22.6 °C | |||
蒸发速率 | 暂无数据 | |||
易燃性(固体,气体) | 暂无数据 | |||
高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 | 暂无数据 | |||
蒸气压 | 0.6±0.7 mmHg at 25°C | |||
蒸气焓 | 46.8±6.0 kJ/mol | |||
密度/相对密度 | 1.3200 | |||
溶于水、甲醇、乙醇,微溶于乙醚、氯仿、苯。 | ||||
正辛醇/水分配系数 | Log Kow (KOWWIN v1.67 estimate) = -1.56
Log Kow (Exper. database match) = -2.11
Exper. Ref: Hansch,C et al. (1995)/ Boiling Pt, Melting Pt, Vapor Pressure Estimations (MPBPWIN v1.42):
Boiling Pt (deg C): 158.06 (Adapted Stein & Brown method)
Melting Pt (deg C): 28.99 (Mean or Weighted MP)
VP(mm Hg,25 deg C): 0.208 (Modified Grain method)
MP (exp database): 132.7 deg C
VP (exp database): 1.20E-05 mm Hg at 25 deg C
Subcooled liquid VP: 0.000139 mm Hg (25 deg C, exp database VP ) | |||
正辛醇空气分配系数 | Log Kow used: -2.11 (exp database)
Log Kaw used: -10.148 (exp database)
Log Koa (KOAWIN v1.10 estimate): 8.038
Log Koa (experimental database): None | |||
自燃温度 | 暂无数据 | |||
分解温度 | 暂无数据 | |||
黏度 | 暂无数据 | |||
暂无数据 | ||||
氧化性 | 暂无数据 | |||
根据碎片估算水溶胶 | Wat Sol (v1.01 est) = 1e+006 mg/L
Wat Sol (Exper. database match) = 545000.00
Exper. Ref: YALKOWSKY,SH (1989) | |||
亨利定律常数(25摄氏度) | Bond Method : 3.65E-010 atm-m3/mole
Group Method: Incomplete
Exper Database: 1.74E-12 atm-m3/mole
Henrys LC [VP/WSol estimate using EPI values]: 3.859E-008 atm-m3 | |||
9.2 其他安全信息 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第10部分:稳定性和反应性 | ||||
10.1 稳定性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.2 危险反应 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.3 应避免的条件 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.4 禁配物 | ||||
强氧化剂 | ||||
10.5 危险的分解产物 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第11部分:毒理学信息 | ||||
11.1 毒理学影响信息 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
呼吸或皮肤过敏 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
生殖毒性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触) | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
吸入危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
附加说明 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第12部分:生态学危害信息 | ||||
12.1 生态毒性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.2 持久性和降解性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.3 快速生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin1 (Linear Model) : 0.7190
Biowin2 (Non-Linear Model) : 0.8962 | ||||
12.4 专家调查生物降解结果 | ||||
Biowin3 (Ultimate Survey Model): 3.0665 (weeks )
Biowin4 (Primary Survey Model) : 3.7611 (days ) | ||||
12.5 MITI生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin5 (MITI Linear Model) : 0.5335
Biowin6 (MITI Non-Linear Model): 0.6882 | ||||
12.6 厌氧生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin7 (Anaerobic Linear Model): 0.8361 | ||||
12.7 现成的生物降解性预测 | ||||
YES | ||||
12.8 碳氢化合物生物降解 | ||||
Structure incompatible with current estimation method! | ||||
12.9 对气溶胶的吸附 | ||||
Vapor pressure (liquid/subcooled): 0.0185 Pa (0.000139 mm Hg)
Log Koa (Koawin est ): 8.038
Kp (particle/gas partition coef. (m3/ug)):
Mackay model : 0.000162
Octanol/air (Koa) model: 2.68E-005 | ||||
12.10 羟基自由基反应 | ||||
OVERALL OH Rate Constant = 2.0000 E-12 cm3/molecule-sec
Half-Life = 5.348 Days (12-hr day; 1.5E6 OH/cm3)
Half-Life = 64.176 Hrs | ||||
12.11 臭氧反应 | ||||
No Ozone Reaction Estimation | ||||
12.12 空气中颗粒物吸附的分数(PHI) | ||||
0.0093 (Junge,Mackay)
Note: the sorbed fraction may be resistant to atmospheric oxidation | ||||
12.13 土壤吸附系数 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.14 碱/酸催化水解(25℃) | ||||
Koc : 4.191
Log Koc: 0.622 / Aqueous Base/Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis (25 deg C) [HYDROWIN v1.67]:
Rate constants can NOT be estimated for this structure!/ | ||||
12.15 利用对数KOW估算生物累积量 | ||||
Log BCF from regression-based method = 0.500 (BCF = 3.162)
log Kow used: -2.11 (expkow database) | ||||
12.16 废水处理中的去除 | ||||
Total removal: 1.85 percent
Total biodegradation: 0.09 percent
Total sludge adsorption: 1.75 percent
Total to Air: 0.00 percent
(using 10000 hr Bio P,A,S) | ||||
12.17 三级逸度模型 | ||||
Mass Amount Half-Life Emissions
(percent) (hr) (kg/hr)
Air 4.1e-005 128 1000
Water 39 360 1000
Soil 60.9 720 1000
Sediment 0.0713 3.24e+003 0
Persistence Time: 579 hr | ||||
12.18 土壤中的迁移性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.19 PBT和VPVB的结果评价 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.20 其他环境有害作用 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第13部分:废弃处置 | ||||
13.1 废物处理 | ||||
None | ||||
None | ||||
第14部分:运输信息 | ||||
14.1 联合国编号 / UN NUMBER | ||||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID: | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IMDG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
14.2 联合国运输名称 / UN PROPER SHIPPING NAME | ||||
欧洲陆运危规: | None | |||
国际海运危规: | None | |||
国际空运危规: | None | |||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID: | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IMDG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID : | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IM0DG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
None | ||||
14.6 特殊防范措施 / SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR USER | ||||
None | ||||
None | ||||
第15部分:法律法规信息 | ||||
适用法规 | ||||
《中华人民共和国安全生产法》、《职业病防治法》、《化学化工实验室安全管理规范》 | ||||
其它的规定 | ||||
《生产安全事故报告和调查处理条例》、《职业病防治法》、《职业安全和卫生法》美国1970 | ||||
第16部分:其他补充信息 | ||||
其他信息 版权所有:BIOFOUNT BEIJING BIO TECH CO.,LTD 公司。许可无限制纸张拷贝,仅限于内部使用。 上述信息视为正确,但不包含所有的信息,仅作为指引使用。本文件中的信息是基于我们目前所知,就正确的安全提示来说适用于本品。该信息不代表对此产品性质的保证。BIOFOUNT公司及其附属公司对任何操作或者接触上述产品而引起的损害不负有任何责任。更多使用条款,参见发票或包装条的反面。 更多销售条款及条件请参见HTTP://WWW.BIO-FOUNT.COM/或发票或装箱单的背面。欲悉详情,请联系:SALES@BIO-FOUNT.COM | ||||
- 相关产品
-
< >
- 推荐产品
-
< >
- 最新产品
-
< >
新闻
怎么做细胞爬片免疫组化染色实验
细胞爬片免疫组化染色,是通过细胞爬片是让玻片浸在细胞培养基内,细胞在玻片上生长,主要用于组织学,免疫组织化学...
2020/7/20 22:04:33
提取病毒RNA的实验方法
提取病毒RNA方法分别有:异硫氰酸胍的提取病毒RNA方法、TRIzol LS提取法、Trizol法提取法等等...
2020/7/22 20:29:26
各种微流控芯片键合方法的优缺点
微流控芯片键合:目前主要有激光焊接、热压键合、胶键合、超音波焊接,每种方法都有各自的优缺点。本文主要介绍聚酯...
2023/7/28 10:43:09

新一代微流控键合解决方案
微流控键合解决方案:微流控芯片制造的一个重要环节,也是最容易被忽视的--芯片键合。其中一个重要因素是:微流控...
2023/7/27 12:44:28
荧光素钾盐使用说明
D-荧光素钾盐(K+)设计用于体外和体内生物发光测定。D-荧光素的质量和纯度对于获得良好和可重复的结果至关重...
2023/7/20 11:05:11
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白)
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白):牛血清白蛋白(BSA)有多种形式,如何选择适合自己的牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是一...
2023/2/14 13:09:18

牛血清白蛋白(BSA)常见问题
牛血清白蛋白(BSA)常见问题:牛血清白蛋白(BSA)在实验室中是通用的,可用于蛋白质印迹、细胞组织培养、P...
2022/10/19 9:39:51
pubmed使用方法(技巧)
pubmed使用方法(技巧):PubMed是一个关于医学问题的学术文章和书籍的数据库。因为它是一份学术期刊,...
2022/10/18 18:06:07
BSA(牛血清白蛋白)
BSA(牛血清白蛋白):牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是一种球状蛋白质,牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是发现于牛血浆中的主要...
2022/10/18 16:48:12
冻干培养细菌的方法
冻干培养细菌的方法:冷冻干燥,也称为冻干或冷冻干燥,是在产品冷冻后除去水分并将其置于真空中的过程。这使得冰可...
2022/10/16 8:27:31




 购物车
购物车 



