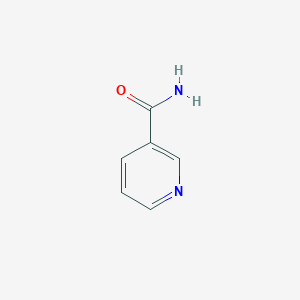
-
Nicotinamide
- names:
Nicotinamide, PARP inhibitor
- CAS号:
98-92-0
MDL Number: MFCD00006395 - MF(分子式): C6H6N2O MW(分子量): 122.12
- EINECS:200-659-6 Reaxys Number:No data available
- Pubchem ID:936 Brand:BIOFOUNT
烟酰胺(98-92-0,Nicotinamide)是一种重要的化合物,可作为辅酶NAD的组分。烟酰胺的主要意义在于预防和/或治疗舌苔和糙皮病。人及大多数动物不能以足以防止营养缺乏的量生产这种化合物,因此必须通过饮食摄入来补充。烟酰胺属于一种称为烟酰胺类的的有机化合物,它们是含有在第3位被羧酰胺基取代的吡啶环的杂环芳香族化合物。
烟酰胺(维生素B3)是一种水溶性维生素,属于维生素B族;目标:维生素B3烟酰胺,也称为烟酰胺和烟酸酰胺,是烟酸的酰胺(维生素B3 /烟酸)。不会降低胆固醇或引起潮红,尽管对于成年人来说,每天超过3 g的剂量烟酰胺可能对肝脏有毒。研究表明烟酰胺具有抗焦虑(抗焦虑)特性。它可能与苯二氮卓类药物相似,它是沉默调节蛋白的激活剂(但在更高剂量时会抑制),据报道可恢复阿尔茨海默氏病转基因小鼠的认知。引起氧化应激.
| 货品编码 | 规格 | 纯度 | 价格 (¥) | 现价(¥) | 特价(¥) | 库存描述 | 数量 | 总计 (¥) |
|---|
| 中文别名 | Nicotinamide(98-92-0);烟酰胺;3吡啶甲酰胺;3-吡啶甲酰胺;维生素B 3;B3,维生素;内酰胺;尼古丁·耶拉米德Jenapharm;烟酰胺;尼古比翁;烟酰胺;尼古丁;Papulex;维生素B 3;维生素B3;维生素PP; |
| 英文别名 | Nicotinamide, PARP inhibitor(CAS:98-92-0);3 Pyridinecarboxamide;3-Pyridinecarboxamide;B 3, Vitamin;B3, Vitamin;Enduramide;Jenapharm, Nicotins?ureamid;Niacinamide;Nicobion;Nicotins?ureamid Jenapharm;Papulex;Vitamin B 3;Vitamin B3;Vitamin PP; |
| CAS号 | 98-92-0 |
| SMILES | c1cc(cnc1)C(=N)O |
| Inchi | InChI=1S/C6H6N2O/c7-6(9)5-2-1-3-8-4-5/h1-4H,(H2,7,9) |
| InchiKey | DFPAKSUCGFBDDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| 分子式 Formula | C6H6N2O |
| 分子量 Molecular Weight | 122.12 |
| 闪点 FP | 150 °C |
| 熔点 Melting point | 128-131°C |
| 沸点 Boiling point | 257.7±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Polarizability极化度 | 13.3±0.5 10-24cm3 |
| 密度 Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| 蒸汽压 Vapor Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| 溶解度Solubility | Soluble in water (1000 g/l) at 20 °C, ethanol (100 mM), glycerol (1 g/10ml), DMSO (100 mM), methanol, butanol, chloroform, and ether (Slightly). |
| 性状 | 白色粉末 |
| 储藏条件 Storage conditions | 2-8°摄氏度密封干燥处保存。 |
烟酰胺(98-92-0,Nicotinamide)毒理性质:
| 生物 | 测试类型 | 路线 | 剂量 | 影响 | 参考 |
| Mutation Data | body fluid assay | ovary/rat | 25 mg/kg | Mar-19 | |
| Mutation Data | Cytogenetic Analysis | intraperitoneal/mouse | 1200 mg/kg | Mar-19 | |
| Mutation Data | DNA inhibition | liver/rat | 20 mmol/L | Mar-19 | |
| Mutation Data | mutation in microorganisms | /Salmonella typhimurium | 5 mg/plate (+enzymatic activation step) | Mar-19 | |
| Mutation Data | sister chromatid exchange | lymphocyte/human | 10 mmol/L | Mar-19 | |
| Mutation Data | sister chromatid exchange | ovary/hamster | 5 mmol/L | Mar-19 | |
| Acute Toxicity Data | In Vitro/Human, endothelium | Inhibitor Concentration (50 percent kill): 50 mmol/L/24H | In Vitro Toxicity Studies: Cell viability (lysosomal damage): neutral red assay etc. | Mar-19 | |
| Acute Toxicity Data | In Vitro/Human, fibroblast | Inhibitor Concentration (50 percent kill): 88 mmol/L/24H | In Vitro Toxicity Studies: Cell viability (lysosomal damage): neutral red assay etc. | Mar-19 | |
| Acute Toxicity Data | In Vitro/Human, liver tumor | Inhibitor Concentration (50 percent kill): 65 mmol/L/24H | In Vitro Toxicity Studies: Cell viability (lysosomal damage): neutral red assay etc. | Mar-19 | |
| Acute Toxicity Data | In Vitro/Human, melanoma | Inhibitor Concentration (50 percent kill): 70 mmol/L/24H | In Vitro Toxicity Studies: Cell viability (lysosomal damage): neutral red assay etc. | Mar-19 |
烟酰胺(98-92-0,Nicotinamide)物理参数:
| 物理特性 | 值 | 单位 | 温度(摄氏度) | 资源 |
| 熔点 | 130 | deg C | EXP | |
| pKa离解常数 | 3.35 | (none) | 20 | EXP |
| log P(辛醇-水) | -0.37 | (none) | EXP | |
| 水溶性 | 5.00E+05 | mg/L | 25 | EXP |
| 蒸汽压力 | 4.20E-04 | mm Hg | 25 | EST |
| 亨利定律常数 | 2.90E-12 | atm-m3/mole | 25 | EST |
| 大气OH速率常数 | 2.34E-12 | cm3/molecule-sec | 25 | EST |
烟酰胺(98-92-0,Nicotinamide)实验注意事项:
1.使用98-92-0实验前需戴好防护眼镜,穿戴防护服和口罩,佩戴手套,避免与皮肤接触。
2.使用98-92-0实验过程中如遇到有毒或者刺激性物质及有害物质产生,必要时实验操作需要手套箱内完成以免对实验人员造成伤害。
3.取样品98-92-0的移液枪头需及时更换,必要时为避免交叉污染尽可能选择滤芯吸头。
4.称量药品时选用称量纸,并无风处取药和称量以免扬撒,试剂的容器使用前务必确保干净,并消毒。
5.取药品98-92-0时尽量采用多个药勺分别使用,使用后清洗干净。
6.实验后产生的废弃物需分类存储,并交于专业生物废气物处理公司处理,以免造成环境污染。
大规格定制:定制产品请将信息发送至sales@bio-fount.com。
Experimental considerations:
1. Wear protective glasses, protective clothing and masks, gloves, and avoid contact with the skin during the experiment.
2. The waste generated after the experiment needs to be stored separately, and handed over to a professional biological waste gas treatment company to avoid environmental pollution.
Tags:烟酰胺试剂,烟酰胺杂质,烟酰胺中间体,烟酰胺密度,烟酰胺旋光度,烟酰胺溶解度,烟酰胺闪点,烟酰胺购买,烟酰胺MSDS,烟酰胺结构式,
| 产品说明 | 烟酰胺(98-92-0)是一种水溶性维生素,烟酰胺是辅酶NAD和NADP的活性成分,烟酰胺溶解度,烟酰胺MSDS,烟酰胺应用等参数详见主页 |
| Introduction | Nicotinamide(98-92-0,烟酰胺)is a water-soluble vitamin. Niacinamide is the active ingredient of the coenzymes NAD and NADP. Niacinamide is also the activator of sirtuin.. |
| Application1 | 烟酰胺是一种B3维生素,通过促进NAD +氧化还原还原和提供NAD +作为催化非氧化还原反应的一类酶的底物,在细胞生理学中发挥重要作用。烟酰胺是SIRT1的抑制剂。 |
| Application2 | |
| Application3 |
烟酰胺(98-92-0,Nicotinamide)药理学:
烟酰胺(98-92-0,Nicotinamide)是无臭或几乎无臭,味苦,易溶于水和乙醇,溶于甘油,溶解度: 1000 g/L 水(20°C) ,1g/1.5ml 乙醇, 1g/10ml 甘油,
烟酰胺是维生素B3的活性形式,是辅酶烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸(NAD)的组成部分。烟酰胺通过增强肿瘤的血流量从而起到化学增敏剂和放射增敏剂的作用,从而减少了肿瘤的缺氧。该试剂还抑制聚(ADP-核糖)聚合酶,该聚合酶涉及通过放射或化学疗法诱导的DNA链断裂的重新结合。 烟酰胺是吡啶羧酰胺,其是吡啶,其中第3位的氢被羧酰胺基团取代。它具有EC 2.4.2.30(NAD(+)ADP-核糖基转移酶)抑制剂,代谢产物,辅因子,抗氧化剂,神经保护剂,EC 3.5.1.98(组蛋白脱乙酰基酶)抑制剂,抗炎剂的作用,Sir2抑制剂,酿酒酵母代谢产物,大肠杆菌代谢产物和小鼠代谢产物。它是吡啶甲酰胺和吡啶生物碱。它来自烟酸。
| 警示图 | |
| 危险性 | warning |
| 危险性警示 | Not Available |
| 安全声明 | H315,H319,H335 |
| 安全防护 | P261,P305+P351+P338 |
| 备注 | 避免吸入,误食以及与皮肤接触 |
烟酰胺(98-92-0,Nicotinamide)危害标识:
| 形图 |  |
| 信号 | Warning |
| GHS危险说明 | Aggregated GHS information provided by 1037 companies from 21 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. |
| Reported as not meeting GHS hazard criteria by 3 of 1037 companies. For more detailed information, please visit ECHA C&L website | |
| Of the 19 notification(s) provided by 1034 of 1037 companies with hazard statement code(s): | |
| H315 (28.72%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] | |
| H319 (99.81%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] | |
| H335 (28.53%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure; Respiratory tract irritation] | |
| Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. | |
| 防范说明代码 | P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, and P501 |
| (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| LiM, Dyda F, Benhar I, Pastan I, Davies DR: Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of Pseudomonas exotoxin A complexed with a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide analog: |
| Pollack M: The role of exotoxin A in pseudomonas disease and immunity. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5 Suppl 5:S979-84. doi:10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s979. [PubMed:6419320] |
| Armstrong S, Merrill AR: Toward the elucidation of the catalytic mechanism of the mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. Biochemistry. 2004 Jan 13;43(1):183-94. doi |
| implications for the activation process and for ADP ribosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jul 9;93(14):6902-6. [PubMed:8692916] |
1.烟酰胺的光保护作用
Diona L. Damian*. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2010, 9, 578–585
Nicotinamide intake, de?ciency and pharmacology Nicotinamide and nicotinic acid (niacin, which is converted to nicotinamide in vivo; Fig. 1) are most abundant in foods such as meats, legumes, nuts, grains, coffee and tea, andinniacin-forti?ed cereals. Nicotinamide is also manufactured in the liver from tryptophan, which is found in eggs, dairy products, ?sh, meat and soybeans and comprises up to 2% of total dietary protein. The tryptophan pathway provides ~50%of total niacin requirements. Recommended daily nicotinamide intake for adults is ~15 mg, and typical commercially available daily supplement doses range from 20–500 mg.
2. Sirtuin的机制和抑制作用:用N e-乙酰赖氨酸类似物探索
Brett M. Hirsch and Weiping Zheng*. Mol. BioSyst., 2011, 7, 16–28
Multiple transcriptional coactivators such as p300, cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB) binding protein (CBP), and p300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF) were shown to possess an intrinsic protein acetyltransferase activity. The yeast transcriptional repressors reduced potassium dependency 3 (Rpd3), histone deacetylase 1 (Hda1), and silent information regulator 2 (Sir2) were shown to possesses a protein deacetylase activity. While acetyl-coenzyme A (AcCoA) is used as the universal cofactor to donate the acetyl group during lysine Ne-acetylation catalyzed by all the protein acetyltransferases, the enzymatic lysine Ne-deacetylation is accomplished by the deacetylase enzymes that use either Zn2+ or b-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (β-NAD+ or just NAD+ as used below throughout this article) as the catalytic cofactor. While the Zn2+-containing metallo-deacetylases catalyze the Zn2+-assisted hydrolysis of the amide bond of the acetyl-lysine side chain to a?ord the deacetylated product and acetic acid, the NAD+-dependent deacetylases achieve the deacetylation of the acetyl-lysine side chain by catalyzing the ultimate transfer of the acetyl group onto the 2’-OH of the nicotinamide ribose of NAD+, which is coupled to the cleavage of nicotinamide from NAD+, thus a?ording three enzymatic products, i.e. nicotinamide, the deacetylated product, and 2’-O-acetyl-ADP-ribose (20 -O-AADPR) (Fig. 1). Rpd3 and Hda1 are the two founding members of the Zn+-containing protein deacetylase enzyme family that also includes the eleven human homologs (HDAC1-11, HDAC stands for histone deacetylase). Sir2 is the founding member of the NAD+-dependent protein deacetylase enzyme family that is also known as the sirtuin family.
3.烟酰胺对心肌细胞缺氧/复氧损伤的保护作用:细胞线粒体代谢的研究
He Wang, Xiaoping Liang,* Guoan Luo, Mingyu Ding and Qionglin Liang*. Mol. BioSyst., 2016, 12, 2257—2264
Nicotinamide, the amide form of nicotinic acid, is the precursor of the coenzymeβNAD, which is an important currency for cell energy metabolism. The protective properties of nicotinamide in enhancement of cell survival as well as longevity, especially in neuroprotection, have been widely discussed. It has been proved to be neuroprotective by poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase inhibition and lipid peroxidation. Furthermore, a nicotinamide-rich diet could up-regulate SUR2A and ATP-sensitive K+ channels in H/R injured mice, thus increasing cardiac resistance to H/R. It has also been proved that nicotinamide could increase the membrane potential of mitochondria, thus improving mitochondrial stress in cardiomyocytes. However, little is known about the role of nicotinamide in metabolism regulation during cardiac H/R injury. We suppose that nicotinamide may preserve mitochondrial NAD-linked respiration and regulate cellular metabolism, especially the mitochondrial metabolism (Fig. 1).
Ren 化学品安全技术说明书 | 版本:1.0 | |||
按照GB/T16483、GB/T17519编制 | 修订日期:10.07.2019 | |||
打印日期:19.02.2020 | ||||
版权所有:范德(北京)生物科技有限责任公司 | 最初编制日期:25.05.2017 | |||
公司网站:WWW.BIO-FOUNT.COM | SDS编号:BIOFOUNT-SY0032 | |||
版权所有:BIOFOUNT BEIJING BIO TECH CO.,LTD | 产品编号:SY0032 | |||
烟酰胺 | ||||
说明书目录 | ||||
第1部分 | 第2部分 | 危险性概述 | ||
第3部分 | 成分/组成信息 | 第4部分 | 急救措施 | |
第5部分 | 消防措施 | 第6部分 | 泄露应急处理 | |
第7部分 | 操作处置与储存 | 第8部分 | 接触控制/个体防护 | |
第9部分 | 理化性质 | 第10部分 | 稳定性和反应性 | |
第11部分 | 毒理学信息 | 第12部分 | 生态学危害信息 | |
第13部分 | 废弃处置 | 第14部分 | 运输信息 | |
第15部分 | 法律法规信息 | 第16部分 | 其他补充信息 | |
第1部分:化学品及企业标识 | ||||
1.1 产品标识 | ||||
烟酰胺 | ||||
ENGLISH NAME: | Nicotinamide | |||
SY0032 | ||||
BIOFOUNT | ||||
98-92-0 | ||||
1.2 安全技术说明书提供者的详情 | ||||
制造商或供应商名称: | ||||
制造地址: | 59 KANGTAI AVENUE BINHAI NEW DISTRICT TIANJIN 300450 TIANJIN CHINA 范德(天津)生物科技有限责任公司 天津市滨海新区康泰大道59号九州通绿谷健康产业园 邮政编码:300450 | |||
电话号码: | ||||
1.3 应急咨询电话 | ||||
紧急联系电话: | ||||
1.4 物质或混合物的推荐用途和限制用途 | ||||
已确认的各用途: | 仅用于科学研发,不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。 | |||
第2部分:危险性概述 | ||||
2.1 GHS危险性类别 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.2 GHS 标签要素,包括防范说明 | ||||
象形图 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
Warning | ||||
H315,H319,H335 | ||||
警告申明 | ||||
避免吸入,误食以及与皮肤接触 | ||||
P261,P305+P351+P338 | ||||
事故响应 | ||||
1.化学品使用过程中,当出现事故或者有紧急情况发生时,当事人应第一时间向应急小组负责人汇报后,由应急小组采取措施防止事态扩大。2.应急小组对受害人采取救护措施。 | ||||
密封干燥处保存。 | ||||
废弃处置 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.3 物理和化学危险 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.4 健康危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.5 环境危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.6 其它危害物 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第3部分:成分/组成信息 | ||||
物质/混合物 | 暂无数据 | |||
3.1 物 质 | ||||
C6H6N2O | ||||
122.12 | ||||
110-91-8 | ||||
EC-编号 | 202-713-4 | |||
根据相应法规,无需披露具体组份。 | ||||
第4部分:急救措施 | ||||
4.1 必要的急救措施描述 | ||||
吸入 | ||||
立即将患者移至空气新鲜处,发现呼吸困难时,必须立即采取吸氧处理,停止呼吸时采取人工呼吸。同时联系及时就医。 | ||||
皮肤接触 | ||||
立即脱去或者剪去污染的衣物,迅速用大量的流动清水冲10-20分钟甚至更长时间后,赴医院就医。 | ||||
眼睛接触 | ||||
立即用大量的流动清水冲10-20分钟后赴医院就医处理。 | ||||
食入 | ||||
误食化学物品后,应立即采取措施进行催吐。1.若误食化学品呈酸性,则可服用大量牛奶和水,促使食如折呕吐。2.若误食化学品呈碱性,则可服用大量牛奶、清水和醋,促使其呕吐,紧急处理后,应及时送至医院进行治疗(仅供参考)。食如者昏迷状态下禁止催吐,以免造成窒息。 | ||||
4.2 最重要的症状和健康影响 | ||||
最重要的已知症状及作用已在标签(参见章节2.2)和/或章节11中介绍 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
4.4 对医生的特别提示 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第5部分:消防措施 | ||||
5.1 灭火介质 | ||||
采用泡沫灭火器、二氧化碳灭火器,避免造成二次污染发生。 | ||||
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
5.3 灭火注意事项及保护措施 | ||||
小规模着火需戴好口罩,防止有毒气体吸入。火灾发生时及时启动应急相应系统撤离至上风口处,并联系当地消防部门灭火。 | ||||
第6部分:泄露应急处理 | ||||
1.泄露后首先启动应急相应系统2.泄露处理前,需穿戴好安全安全防护鞋、穿戴好安全防护手套(强酸性物质需穿戴防酸碱手套)、根据吸入危险性穿戴相应防护面罩。 有关个人防护,请看第8部分。 | ||||
6.2 环境保护措施 | ||||
参照《范德生物化学废弃物处理方法》处理,防止对环境造成危害,处理后交由有资质的废弃物处理结构进行处理,以免造成环境污染。 | ||||
参照《范德生物化学品废弃物处理方法》对泄露的化学品进行处理,处理前需用化学品吸附岩棉对泄露区域进行围挡,形成“围堰”防止泄露扩大。 | ||||
6.4 参考其他部分 | ||||
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。 | ||||
第7部分:操作处置与储存 | ||||
7.1 安全操作的注意事项 | ||||
使用过程请穿戴好口罩,手套等防护用品,避免与皮肤接触、吸入、误食危险。 有关预防措施,请参见章节2.2。 | ||||
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性 | ||||
暂时无法提供详细数据,尽可能避免与其他化合物混合存储,避光、通风处存储。 | ||||
第8部分:接触控制/个体防护 | ||||
8.1 控制参数 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
8.2 暴露控制 | ||||
适当的技术控制 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
个体防护装备 | ||||
一般情况下穿戴安全防护眼镜即可,如有飞溅液体、粉末产生时,请佩戴防溅面罩进行防护。穿戴的防护用品需取得如:GB、NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 等相关认证。 | ||||
手套脱去注意事项:手套在使用前必须进行检查,请使用正确的方法脱除手套(不接触手套外部表面),避免身体任何皮肤部位接触到此产品。根据相关法律法规和实验室管理规范制度,手套使用过后,请将被污染的手套谨慎处理,工作后清洗并吹干双手。 所选择的保护手套必须符合法规《劳动防护用品配备标准》、(EU)2016/425以及从此类法规衍生出来的EN 374标准规范。 完全接触保护要求: 手套材料:丁腈橡胶 手套最小的层厚度:0.11 MM 手套溶剂渗透时间:480 分钟 飞溅保护要求: 材料:丁腈橡胶 最小的层厚度 0.11 MM 溶剂渗透时间:480 分钟 如果以溶剂形式应用或与其它物质混合应用,或在不同于《劳动防护用品配备标准》,EN 374规定的条件下应用,请与EC批准的手套的供应商联系。该条只是作为推荐性建议,如遇特殊情况,务必请熟悉该产品属性的专家,选取相关防护用品。此条建议不应该被认定为适应所有特殊条件防护,请根据所处工作条件请求专业工程师指导采取相应防护措施。 | ||||
选择身体部分的防护措施,需要根据危险物质的类型、浓度、量以及特定的工作环境。身体部分防护设备、防护服的类型,必须根据使用者工作场所中的危险物质的浓度、数量进行选择。 | ||||
一般情况下穿戴普通的医用口罩保护呼吸系统即可。有酸雾产生式活性炭类口罩起不到防护作用,如需对粉尘造成损害进行防护时,请采用N95型(US)或P1型(EN 143)类口罩或者防尘面具。特殊情况下使用自吸式呼吸器时,使用的呼吸器必须对呼吸器密闭性、空气供应系统、供气压进行测试,当然呼吸器需通过强制认证标准如:GB、NIOSH(US)、CEN(EU)。 | ||||
环境暴露的控制 | ||||
不要让产品进入下水道。 | ||||
第9部分:理化特性 | ||||
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息 | ||||
形状:暂无数据 | ||||
颜色:暂无数据 | ||||
气味 | 暂无数据 | |||
气味阈值 | 暂无数据 | |||
暂无数据 | ||||
128-131°C | ||||
初沸点和沸程 | 257.7±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |||
闪点 | 150 °C | |||
蒸发速率 | 暂无数据 | |||
易燃性(固体,气体) | 暂无数据 | |||
高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 | 暂无数据 | |||
蒸气压 | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C | |||
蒸气焓 | 52.3±3.0 kJ/mol | |||
密度/相对密度 | 1.2040 | |||
Soluble in water (1000 g/l) at 20 °C, ethanol (100 mM), glycerol (1 g/10ml), DMSO (100 mM), methanol, butanol, chloroform, and ether (Slightly). | ||||
正辛醇/水分配系数 | Log Kow (KOWWIN v1.67 estimate) = -0.45
Log Kow (Exper. database match) = -0.37
Exper. Ref: Hansch,C et al. (1995)/ Boiling Pt, Melting Pt, Vapor Pressure Estimations (MPBPWIN v1.42):
Boiling Pt (deg C): 297.54 (Adapted Stein & Brown method)
Melting Pt (deg C): 99.37 (Mean or Weighted MP)
VP(mm Hg,25 deg C): 0.000198 (Modified Grain method)
MP (exp database): 130 deg C
BP (exp database): 157 @ 0.0005 mm Hg deg C
Subcooled liquid VP: 0.00222 mm Hg (25 deg C, Mod-Grain method) | |||
正辛醇空气分配系数 | Log Kow used: -0.37 (exp database)
Log Kaw used: -9.926 (HenryWin est)
Log Koa (KOAWIN v1.10 estimate): 9.556
Log Koa (experimental database): None | |||
自燃温度 | 暂无数据 | |||
分解温度 | 暂无数据 | |||
黏度 | 暂无数据 | |||
暂无数据 | ||||
氧化性 | 暂无数据 | |||
根据碎片估算水溶胶 | Wat Sol (v1.01 est) = 1e+006 mg/L
Wat Sol (Exper. database match) = 500000.00
Exper. Ref: MERCK INDEX (1996) | |||
亨利定律常数(25摄氏度) | Bond Method : 2.90E-012 atm-m3/mole
Group Method: Incomplete
Henrys LC [VP/WSol estimate using EPI values]: 3.184E-009 atm-m3 | |||
9.2 其他安全信息 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第10部分:稳定性和反应性 | ||||
10.1 稳定性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.2 危险反应 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.3 应避免的条件 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.4 禁配物 | ||||
强氧化剂 | ||||
10.5 危险的分解产物 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第11部分:毒理学信息 | ||||
11.1 毒理学影响信息 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
呼吸或皮肤过敏 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
生殖毒性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触) | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
吸入危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
附加说明 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第12部分:生态学危害信息 | ||||
12.1 生态毒性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.2 持久性和降解性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.3 快速生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin1 (Linear Model) : 0.7450
Biowin2 (Non-Linear Model) : 0.9111 | ||||
12.4 专家调查生物降解结果 | ||||
Biowin3 (Ultimate Survey Model): 2.6609 (weeks-months)
Biowin4 (Primary Survey Model) : 3.8582 (days ) | ||||
12.5 MITI生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin5 (MITI Linear Model) : 0.4748
Biowin6 (MITI Non-Linear Model): 0.4767 | ||||
12.6 厌氧生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin7 (Anaerobic Linear Model): 0.5276 | ||||
12.7 现成的生物降解性预测 | ||||
NO | ||||
12.8 碳氢化合物生物降解 | ||||
Structure incompatible with current estimation method! | ||||
12.9 对气溶胶的吸附 | ||||
Vapor pressure (liquid/subcooled): 0.296 Pa (0.00222 mm Hg)
Log Koa (Koawin est ): 9.556
Kp (particle/gas partition coef. (m3/ug)):
Mackay model : 1.01E-005
Octanol/air (Koa) model: 0.000883 | ||||
12.10 羟基自由基反应 | ||||
OVERALL OH Rate Constant = 2.3373 E-12 cm3/molecule-sec
Half-Life = 4.576 Days (12-hr day; 1.5E6 OH/cm3)
Half-Life = 54.915 Hrs | ||||
12.11 臭氧反应 | ||||
No Ozone Reaction Estimation | ||||
12.12 空气中颗粒物吸附的分数(PHI) | ||||
0.000588 (Junge,Mackay)
Note: the sorbed fraction may be resistant to atmospheric oxidation | ||||
12.13 土壤吸附系数 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.14 碱/酸催化水解(25℃) | ||||
Koc : 51.56
Log Koc: 1.712 / Aqueous Base/Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis (25 deg C) [HYDROWIN v1.67]:
Rate constants can NOT be estimated for this structure!/ | ||||
12.15 利用对数KOW估算生物累积量 | ||||
Log BCF from regression-based method = 0.500 (BCF = 3.162)
log Kow used: -0.37 (expkow database) | ||||
12.16 废水处理中的去除 | ||||
Total removal: 1.85 percent
Total biodegradation: 0.09 percent
Total sludge adsorption: 1.76 percent
Total to Air: 0.00 percent
(using 10000 hr Bio P,A,S) | ||||
12.17 三级逸度模型 | ||||
Mass Amount Half-Life Emissions
(percent) (hr) (kg/hr)
Air 4.06e-005 110 1000
Water 46.2 900 1000
Soil 53.7 1.8e+003 1000
Sediment 0.089 8.1e+003 0
Persistence Time: 976 hr | ||||
12.18 土壤中的迁移性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.19 PBT和VPVB的结果评价 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.20 其他环境有害作用 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第13部分:废弃处置 | ||||
13.1 废物处理 | ||||
None | ||||
None | ||||
第14部分:运输信息 | ||||
14.1 联合国编号 / UN NUMBER | ||||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID: | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IMDG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
14.2 联合国运输名称 / UN PROPER SHIPPING NAME | ||||
欧洲陆运危规: | None | |||
国际海运危规: | None | |||
国际空运危规: | None | |||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID: | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IMDG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID : | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IM0DG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
None | ||||
14.6 特殊防范措施 / SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR USER | ||||
None | ||||
None | ||||
第15部分:法律法规信息 | ||||
适用法规 | ||||
《中华人民共和国安全生产法》、《职业病防治法》、《化学化工实验室安全管理规范》 | ||||
其它的规定 | ||||
《生产安全事故报告和调查处理条例》、《职业病防治法》、《职业安全和卫生法》美国1970 | ||||
第16部分:其他补充信息 | ||||
其他信息 版权所有:BIOFOUNT BEIJING BIO TECH CO.,LTD 公司。许可无限制纸张拷贝,仅限于内部使用。 上述信息视为正确,但不包含所有的信息,仅作为指引使用。本文件中的信息是基于我们目前所知,就正确的安全提示来说适用于本品。该信息不代表对此产品性质的保证。BIOFOUNT公司及其附属公司对任何操作或者接触上述产品而引起的损害不负有任何责任。更多使用条款,参见发票或包装条的反面。 更多销售条款及条件请参见HTTP://WWW.BIO-FOUNT.COM/或发票或装箱单的背面。欲悉详情,请联系:SALES@BIO-FOUNT.COM | ||||
- 相关产品
-
< >
- 推荐产品
-
< >
- 最新产品
-
< >
新闻
怎么做细胞爬片免疫组化染色实验
细胞爬片免疫组化染色,是通过细胞爬片是让玻片浸在细胞培养基内,细胞在玻片上生长,主要用于组织学,免疫组织化学...
2020/7/20 22:04:33
提取病毒RNA的实验方法
提取病毒RNA方法分别有:异硫氰酸胍的提取病毒RNA方法、TRIzol LS提取法、Trizol法提取法等等...
2020/7/22 20:29:26
各种微流控芯片键合方法的优缺点
微流控芯片键合:目前主要有激光焊接、热压键合、胶键合、超音波焊接,每种方法都有各自的优缺点。本文主要介绍聚酯...
2023/7/28 10:43:09

新一代微流控键合解决方案
微流控键合解决方案:微流控芯片制造的一个重要环节,也是最容易被忽视的--芯片键合。其中一个重要因素是:微流控...
2023/7/27 12:44:28
荧光素钾盐使用说明
D-荧光素钾盐(K+)设计用于体外和体内生物发光测定。D-荧光素的质量和纯度对于获得良好和可重复的结果至关重...
2023/7/20 11:05:11
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白)
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白):牛血清白蛋白(BSA)有多种形式,如何选择适合自己的牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是一...
2023/2/14 13:09:18

牛血清白蛋白(BSA)常见问题
牛血清白蛋白(BSA)常见问题:牛血清白蛋白(BSA)在实验室中是通用的,可用于蛋白质印迹、细胞组织培养、P...
2022/10/19 9:39:51
pubmed使用方法(技巧)
pubmed使用方法(技巧):PubMed是一个关于医学问题的学术文章和书籍的数据库。因为它是一份学术期刊,...
2022/10/18 18:06:07
BSA(牛血清白蛋白)
BSA(牛血清白蛋白):牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是一种球状蛋白质,牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是发现于牛血浆中的主要...
2022/10/18 16:48:12
冻干培养细菌的方法
冻干培养细菌的方法:冷冻干燥,也称为冻干或冷冻干燥,是在产品冷冻后除去水分并将其置于真空中的过程。这使得冰可...
2022/10/16 8:27:31




 购物车
购物车 



