- names:
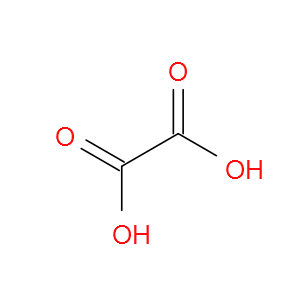
Oxalic acid
- CAS号:
144-62-7
MDL Number: MFCD00002573 - MF(分子式): C2H2O4 MW(分子量): 90.03
- EINECS:205-634-3 Reaxys Number:No data available
- Pubchem ID:24884364 Brand:BIOFOUNT
草酸(144-62-7,Oxalic acid)是一种α,ω-二羧酸,其乙烷在位置1和2,具有一个角色作为人代谢物,植物代谢物和藻类代谢物取代的羧基。它是草酸酯(1-)和草酸酯的共轭酸。草酸以固体,可溶(溶于水)和中等酸性化合物(基于其pKa)存在 ,血液和汗液中发现。在细胞内,草酸主要位于过氧化物酶体中。草酸还是其他转化生成物的母体化合物,包括但不取代草酰辅酶A,草酸甲酯和草酰胺。在人体外部,草酸成为这些食品消费的潜在生物标志物。草酸是一种潜在的有毒化合物。草酸被发现与被称为血液草酸还与多种先天性代谢疾病有关,包括富马酸缺乏症,原发性高草酸尿症I和乙醇酸尿症。草酸是还原剂,向元素或化合物添加电子的材料,即降低其价态的正性。
| 货品编码 | 规格 | 纯度 | 价格 (¥) | 现价(¥) | 特价(¥) | 库存描述 | 数量 | 总计 (¥) |
|---|
| 中文别名 | 草酸(144-62-7),无水草酸,酢浆草酸;修酸;乙二酸;草酸,无水无水草酸; |
| 英文别名 | Oxalic acid(144-62-7);Oxalic acid Analytical Titrant; |
| CAS号 | 144-62-7 |
| Inchi | InChI=1S/C2H2O4/c3-1(4)2(5)6/h(H,3,4)(H,5,6) |
| InchiKey | MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| 分子式 Formula | C2H2O4 |
| 分子量 Molecular Weight | 90.03 |
| 溶解度Solubility | |
| 性状 | 粉末 |
| 储藏条件 Storage conditions | Store at 4°C,-4℃下存储更优 |
草酸(144-62-7,Oxalic acid)毒理性质:
| 生物 | 测试类型 | 路线 | 剂量 | 影响 | 参考 |
| Skin and Eye Irritation | eye /rabbit | 250 µg/24H | severe | Dec-18 | |
| Skin and Eye Irritation | eye /rabbit | 100 mg/4S rinse | severe | Dec-18 | |
| Skin and Eye Irritation | skin /rabbit | 500 mg/24H | mild | Dec-18 | |
| Reproductive Effects | oral/mouse | 8400 mg/kg (7D male/7D pre-21D pregnant) | Reproductive: Effects on fertility: Other measures of fertility; Reproductive: Effects on embryo or fetus: Fetotoxicity (except death, e.g., stunted fetus) | Dec-18 | |
| Reproductive Effects | oral/mouse | 9.63 gm/kg (7D male/7D prior to copulation/21D pregnant) | Reproductive: Effects on fertility: Other measures of fertility; Reproductive: Effects on newborn: Growth statistics (e.g., reduced weight gain) | Dec-18 | |
| Reproductive Effects | oral/mouse | 275 mg/kg (multigenerations) | Reproductive: Specific developmental abnormalities: Urogenital system; Reproductive: Effects on newborn: Live birth index (Litter size (e.g., # fetuses per litter; measured after birth) | Dec-18 | |
| Acute Toxicity Data | In Vitro/Human, leukemia cells | Inhibitor Concentration (50 percent kill): 310.33 mg/L/24H | In Vitro Toxicity Studies: Other assays | Dec-18 | |
| Acute Toxicity Data | In Vitro/Human, liver tumor | Inhibitor Concentration (50 percent kill): 10 mmol/L/24H | In Vitro Toxicity Studies: Cell protein synthesis | Dec-18 | |
| Acute Toxicity Data | In Vitro/Human, lymphocyte | Inhibitor Concentration (30 percent kill): >200 mg/L/45H | In Vitro Toxicity Studies: Cell viability (dye exclusion): trypan blue assay etc. | Dec-18 | |
| Acute Toxicity Data | In Vitro/Human, lymphocyte | Inhibitor Concentration (50 percent kill): >200 mg/L/45H | In Vitro Toxicity Studies: Other assays | Dec-18 | |
| Acute Toxicity Data | In Vitro/Human, monocyte | Inhibitor Concentration Low: 931 mg/L/2H | In Vitro Toxicity Studies: Other assays | Dec-18 | |
| Acute Toxicity Data | In Vitro/Non-mammalian species, fibroblast | Inhibitor Concentration (50 percent kill): 14.17 mmol/L/24H | In Vitro Toxicity Studies: Cell counting | Dec-18 | |
| Acute Toxicity Data | intraperitoneal/mouse | lethal dose (50 percent kill): 270 mg/kg | Dec-18 | ||
| Acute Toxicity Data | oral/Dog | lowest published lethal dose: 1 gm/kg | Dec-18 | ||
| Acute Toxicity Data | oral/woman | lowest published lethal dose: 600 mg/kg | Gastrointestinal: Changes in structure or function of esophagus; Gastrointestinal: Hypermotility, diarrhea; Gastrointestinal: Other changes | Dec-18 | |
| Acute Toxicity Data | subcutaneous/cat | lowest published lethal dose: 112 mg/kg | Dec-18 | ||
| Acute Toxicity Data | subcutaneous/frog | lowest published lethal dose: 757 mg/kg | Dec-18 | ||
| Acute Toxicity Data | unreported route/rat | lethal dose (50 percent kill): 382 mg/kg | Dec-18 | ||
| Other Multiple Dose Data | intraperitoneal/rat | lowest published toxic dose: 225 mg/kg/5D- intermittent | Liver: Other changes; Blood: Other changes; Biochemical: Metabolism (intermediary): Lipids including transport | Dec-18 | |
| Other Multiple Dose Data | oral/mouse | lowest published toxic dose: 2268 mg/kg/14D- continuous | Behavioral: Fluid intake | Dec-18 | |
| Other Multiple Dose Data | oral/mouse | lowest published toxic dose: 40425 mg/kg/21W- continuous | Related to Chronic Data: Changes in prostate weight | Dec-18 | |
| Other Multiple Dose Data | oral/rat | lowest published toxic dose: 175 gm/kg/70D- continuous | Endocrine: Changes in thyroid weight; Musculoskeletal: Other changes; Nutritional and Gross Metabolic: Weight loss or decreased weight gain | Dec-18 |
草酸(144-62-7,Oxalic acid)实验注意事项:
1.使用144-62-7实验前需戴好防护眼镜,穿戴防护服和口罩,佩戴手套,避免与皮肤接触。
2.使用144-62-7实验过程中如遇到有毒或者刺激性物质及有害物质产生,必要时实验操作需要手套箱内完成以免对实验人员造成伤害。
3.取样品144-62-7的移液枪头需及时更换,必要时为避免交叉污染尽可能选择滤芯吸头。
4.称量药品时选用称量纸,并无风处取药和称量以免扬撒,试剂的容器使用前务必确保干净,并消毒。
5.取药品144-62-7时尽量采用多个药勺分别使用,使用后清洗干净。
6.实验后产生的废弃物需分类存储,并交于专业生物废气物处理公司处理,以免造成环境污染。
大规格定制:定制产品请将信息发送至sales@bio-fount.com。
Experimental considerations:
1. Wear protective glasses, protective clothing and masks, gloves, and avoid contact with the skin during the experiment.
2. The waste generated after the experiment needs to be stored separately, and handed over to a professional biological waste gas treatment company to avoid environmental pollution.
Tags:草酸试剂,草酸合成,草酸杂质,草酸密度,草酸中间体,草酸溶解度,草酸旋光度,草酸购买,草酸MSDS,草酸结构式,
| 产品说明 | 草酸(144-62-7)是存在于许多植物和蔬菜中的一种强酸,草酸常被用作分析试剂和一般还原剂.草酸溶解度,草酸msds,草酸结构式详见主页. |
| Introduction | 草酸(144-62-7,Oxalic acid) is a strong acid found in many plants and vegetables. It is often used as an analytical reagent and general reducing agent. |
| Application1 | 草酸是通过乙醛酸或抗坏血酸的代谢在体内产生的。 草酸不被代谢而是通过尿液排出体外。 用作分析试剂和一般还原剂。 |
| Application2 | Oxalic acid was used:· in the synthesis of hemicellulose hydrolysates of yellow poplars;· in the synthesis of three-dimensionally ordered macroporous metal oxides or carbonates via templating with polystyrene spheres;· as supporting electrolyte in the electrochemical synthesis of polyaniline-polypyrrole composite coatings. |
| Application3 |
草酸(144-62-7,Oxalic acid)药理学:
※草酸是无味的白色固体。下沉并与水混合。 草酸是一种α,ω-二羧酸,其乙烷在位置1和2,具有一个角色作为人代谢物,植物代谢物和藻类代谢物取代的羧基。
※它是草酸酯(1-)和草酸酯的共轭酸。 草酸,也称为草酸酯或乙二酸,属于称为二羧酸及其衍生物的有机化合物。这些是恰好含有两个羧酸基团的有机化合物。草酸以固体,可溶(溶于水)和中等酸性化合物(基于其pKa)存在。草酸已经在大多数人体组织中发现,并且也主要在唾液,尿液,血液和汗液中发现。在细胞内,草酸主要位于过氧化物酶体中。草酸还是其他转化产物的母体化合物,包括但不限于草酰辅酶A,草酸甲酯和草酰胺。在人体外部,草酸可用于多种食品中,例如越橘,四棱豆,罂粟和波士莓。草酸成为这些食品消费的潜在生物标志物。草酸是一种潜在的有毒化合物。草酸被发现与被称为血液透析的疾病有关。草酸还与多种先天性代谢疾病有关,包括富马酸缺乏症,原发性高草酸尿症I和乙醇酸尿症。
※草酸是还原剂,向元素或化合物添加电子的材料,即降低其价态的正性。草酸存在于许多植物和蔬菜中。 草酸是通过乙醛酸或抗坏血酸的代谢在体内产生的。 草酸不被代谢而是通过尿液排出体外。 用作分析试剂和一般还原剂。
草酸(144-62-7,Oxalic acid)物理属性:
| 物理特性 | 值 | 单位 | 温度(摄氏度) | 资源 |
| Melting Point | 189.5 dec | deg C | EXP | |
| log P (octanol-water) | -2.22 | (none) | EST | |
| Water Solubility | 2.20E+05 | mg/L | 25 | EXP |
| Vapor Pressure | 2.34E-04 | mm Hg | 25 | EXP |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.43E-10 | atm-m3/mole | 25 | EXP |
| Atmospheric OH Rate Constant | 7.20E-14 | cm3/molecule-sec | 25 | EST |
| 警示图 | |
| 危险性 | warning |
| 危险性警示 | 有机化合物; 食物毒素;植物毒素 代谢物 家庭毒素;工业/工作场所毒素;天然化合物 还原剂毒素 |
| 安全声明 | H318 |
| 安全防护 | P280,P305+P351+P338 |
| 备注 | 避免吸入,误食以及与皮肤接触 |
草酸(144-62-7,Oxalic acid)危害标识:
| 象形图 |  |
| 信号 | Warning |
| GHS危险说明 | H302: Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] |
| H312: Harmful in contact with skin [Warning Acute toxicity, dermal] | |
| 防范说明代码 | P264, P270, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P312, P322, P330, P363, and P501 |
| (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| Cessna SG, et al. Oxalic acid, a pathogenicity factor for Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, suppresses the oxidative burst of the host plant. Plant Cell. 2000 Nov;12(11):2191-200. |
草酸(144-62-7,Oxalic acid)参考文献:
1、Investigations on the oxalic acid content of honey from oxalic acid treated and untreated bee colonies European Food Research and Technology 2003
Varroa destructor, an ectoparasitic mite, is one of the major pests of honeybees in many parts of the world. In order to keep bee colonies alive and productive, effective biological, biotechnical, or acaricidal control measures are necessary. Oxalic acid is one substance under discussion to replace synthetic acaricides (e.g. pyrethroids, organophosphates) to minimize the risk of residues in bee products. The application of oxalic acid based solutions (Bienenwohl or a self-prepared oxalic acid solution with sugar) to control Varroa destructor resulted in no relevant changes in the oxalic acid content of honey produced the following year, compared with honey samples from untreated colonies from the same location. The range of oxalic acid content in honey was 5–68 mg/kg in oxalic acid treated and 5–65 mg/kg in untreated colonies. The oxalic acid content of the honey was positively correlated with its electrical conductivity and thus with its original nectar or honeydew source.
2、A new approach to recycle oxalic acid during lignocellulose pretreatment for xylose production Biotechnology for Biofuels 2018
Influences of reaction temperature and time on hydrolysis efficiency The reaction temperatures of DOAP were 130, 140 and 150 °C, the reaction time of DOAP was 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 and 2.5 h, and the oxalic acid concentration was 100 mmol/L. After this pretreatment, the contents of arabinose, xylose and glucose in the hydrolysate are shown in Fig. 1. The contents of arabinose and xylose showed an increasing tendency under 130 °C and 140 °C, but they displayed the tendency of increasing firstly and then decreasing under the 150 °C pretreatment condition (Fig. 1a, b). Among these pretreatments, the maximum xylose content was achieved up to 250.48 mg/g under the pretreatment condition with 140 °C reaction temperature and 2.5-h reaction time, correspondingly, the arabinose and glucose contents were 36.28 mg/g and 29.06 mg/g, respectively. In other words, 79.9% xylose and 91.0% arabinose could be released from the cell wall of corncob, indicating that oxalic acid had the high selectivity to hydrolyse xylan-type hemicellulose into C5 sugars (xylose and arabinose), and the branched chain mainly arabinose was easily broken down when xylan as the main chain was destroyed [20]. Under 130, 140 and 150 °C pretreatment conditions, the content of glucose presented an increasing tendency (Fig. 1c). The possible reason of this result was that a part of cellulose was hydrolysed to glucose when the severe pretreatment conditions were used [20]. To get high pentose yield, the optimized reaction temperature and time were set to 140 °C and 2.5 h, respectively, and the compositions of the hydrolysate were investigated under the pretreatment conditions of 10, 50, 100, 150 and 200 mmol/L oxalic acid concentration.
3、Applicability of Electroanalysis for Monitoring Oxalic Acid (OA) Concentration During its Electrochemical Oxidation at Different Electrode Materials Electrocatalysi2013
The electrochemical oxidation (EO) of oxalic acid (OA) has been studied in acidic media at Ti/PbO2, highly boron-doped diamond (BDD), Pt, and graphite electrodes by linear polarization and galvanostatic electrolyses applying a current of 60 mA cm−2. The concentration of OA during EO was monitored by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) using glassy carbon electrode and the results were also confirmed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The experimental results of galvanostatic electrolyses showed that the performances of the process dramatically depend on the anodic material and in particular, the removal efficiencies obtained at Ti/PbO2, graphite, BDD, and Pt anodes were 90, 85, 80, and 78 %, respectively. Furthermore, DPV analyses compared with HPLC method achieved good fit, confidence intervals, and limits.
4、Oxalic acid: a prospective tool for reducing Varroa mite populations in package bees Experimental and Applied Acarology 2009 19184581
Numerous studies have investigated using oxalic acid (OA) to control Varroa mites in honey bee colonies. In contrast, techniques for treating package bees with OA have not been investigated. The goal of this study was to develop a protocol for using OA to reduce mite infestation in package bees. We made 97 mini packages of Varroa-infested adult bees. Each package contained 1,613 ± 18 bees and 92 ± 3 mites, and represented an experimental unit. We prepared a 2.8% solution of OA by mixing 35 g OA with 1 l of sugar water (sugar:water = 1:1; w:w). Eight treatments were assigned to the packages based on previous laboratory bioassays that characterized the acute contact toxicity of OA to mites and bees. We administered the treatments by spraying the OA solution directly on the bees through the mesh screen cage using a pressurized air brush and quantified mite and bee mortality over a 10-day period. Our results support applying an optimum volume of 3.0 ml of a 2.8% OA solution per 1,000 bees to packages for effective mite control with minimal adult bee mortality. The outcome of our research provides beekeepers and package bee shippers guidance for using OA to reduce mite populations in package bees.
5、Brood removal or queen caging combined with oxalic acid treatment to control varroa mites (Varroa destructor) in honey bee colonies (Apis mellifera) Apidologie 2017
Statistical analysis Statistical analysis and figure generation were conducted with R environment (R Core Team 2011). Variables of this study included (1) bee mortality, (2) varroa counts, (3) brood removal, and (4) queen caging. All variables were first tested for normality using the Shapiro-Wilk test and were not normally distributed. We attempted to normalize our data by log-transformation and repeated the Shapiro-Wilk test with Q-Q plots to visualize the data distribution. Although log transformation failed to normalize our dataset, per date data were close to normality, and analysis of variance (ANOVA) was carried out at a 95% confidence level. ANOVA is not very sensitive to moderate deviations from normality (Glass et al. 1972; Harwell et al. 1992; Lix et al. 1996), and significant results were double-checked with nonparametric tests. Principal component analyses (PCA) were carried out using “Devtools” Package as well as “FactoMine” to calculate the percentage of the variability expressed in three-dimensional space and to study the clusters and groups based on their overall resemblance. Outlier values were not omitted from the datasets and were treated as such to fairly assess the experimental variables. Results Laboratory experiment Measurements of caged bee mortality from the three OA treatments were made over the course of the 13-day laboratory experiment and again at 4 days after the last OA treatment. These were compared against mortality from the Apistan®-treated group and the control group. Observation time of the 13-day included caged bee mortality between OA treatments and 4 days after the last OA treatment as well as mortality induced by the Apistan® strips and the control treatment. None of the OA concentrations differed significantly in bee mortality (Figure 2), and the Apistan®-treated group was the only one that exhibited significantly higher bee mortality compared to the control (F = 2.7, n = 390, df = 4; P = 0.02) (Figure 3).
Ren 化学品安全技术说明书 | 版本:1.0 | |||
按照GB/T16483、GB/T17519编制 | 修订日期:10.07.2019 | |||
打印日期:19.02.2020 | ||||
版权所有:范德(北京)生物科技有限责任公司 | 最初编制日期:25.05.2017 | |||
公司网站:WWW.BIO-FOUNT.COM | SDS编号:BIOFOUNT-JT12033 | |||
版权所有:BIOFOUNT BEIJING BIO TECH CO.,LTD | 产品编号:JT12033 | |||
无水草酸 | ||||
说明书目录 | ||||
第1部分 | 第2部分 | 危险性概述 | ||
第3部分 | 成分/组成信息 | 第4部分 | 急救措施 | |
第5部分 | 消防措施 | 第6部分 | 泄露应急处理 | |
第7部分 | 操作处置与储存 | 第8部分 | 接触控制/个体防护 | |
第9部分 | 理化性质 | 第10部分 | 稳定性和反应性 | |
第11部分 | 毒理学信息 | 第12部分 | 生态学危害信息 | |
第13部分 | 废弃处置 | 第14部分 | 运输信息 | |
第15部分 | 法律法规信息 | 第16部分 | 其他补充信息 | |
第1部分:化学品及企业标识 | ||||
1.1 产品标识 | ||||
无水草酸 | ||||
ENGLISH NAME: | Oxalic acid Analytical Titrant | |||
JT12033 | ||||
BIOFOUNT | ||||
144-62-7 | ||||
1.2 安全技术说明书提供者的详情 | ||||
制造商或供应商名称: | ||||
制造地址: | 59 KANGTAI AVENUE BINHAI NEW DISTRICT TIANJIN 300450 TIANJIN CHINA 范德(天津)生物科技有限责任公司 天津市滨海新区康泰大道59号九州通绿谷健康产业园 邮政编码:300450 | |||
电话号码: | ||||
1.3 应急咨询电话 | ||||
紧急联系电话: | ||||
1.4 物质或混合物的推荐用途和限制用途 | ||||
已确认的各用途: | 仅用于科学研发,不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。 | |||
第2部分:危险性概述 | ||||
2.1 GHS危险性类别 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.2 GHS 标签要素,包括防范说明 | ||||
象形图 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
Danger | ||||
H318 | ||||
警告申明 | ||||
避免吸入,误食以及与皮肤接触 | ||||
P280,P305+P351+P338 | ||||
事故响应 | ||||
1.化学品使用过程中,当出现事故或者有紧急情况发生时,当事人应第一时间向应急小组负责人汇报后,由应急小组采取措施防止事态扩大。2.应急小组对受害人采取救护措施。 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
废弃处置 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.3 物理和化学危险 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.4 健康危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.5 环境危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.6 其它危害物 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第3部分:成分/组成信息 | ||||
物质/混合物 | 暂无数据 | |||
3.1 物 质 | ||||
C2H2O4 | ||||
90.03 | ||||
110-91-8 | ||||
EC-编号 | 205-634-3 | |||
根据相应法规,无需披露具体组份。 | ||||
第4部分:急救措施 | ||||
4.1 必要的急救措施描述 | ||||
吸入 | ||||
立即将患者移至空气新鲜处,发现呼吸困难时,必须立即采取吸氧处理,停止呼吸时采取人工呼吸。同时联系及时就医。 | ||||
皮肤接触 | ||||
立即脱去或者剪去污染的衣物,迅速用大量的流动清水冲10-20分钟甚至更长时间后,赴医院就医。 | ||||
眼睛接触 | ||||
立即用大量的流动清水冲10-20分钟后赴医院就医处理。 | ||||
食入 | ||||
误食化学物品后,应立即采取措施进行催吐。1.若误食化学品呈酸性,则可服用大量牛奶和水,促使食如折呕吐。2.若误食化学品呈碱性,则可服用大量牛奶、清水和醋,促使其呕吐,紧急处理后,应及时送至医院进行治疗(仅供参考)。食如者昏迷状态下禁止催吐,以免造成窒息。 | ||||
4.2 最重要的症状和健康影响 | ||||
最重要的已知症状及作用已在标签(参见章节2.2)和/或章节11中介绍 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
4.4 对医生的特别提示 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第5部分:消防措施 | ||||
5.1 灭火介质 | ||||
采用泡沫灭火器、二氧化碳灭火器,避免造成二次污染发生。 | ||||
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
5.3 灭火注意事项及保护措施 | ||||
小规模着火需戴好口罩,防止有毒气体吸入。火灾发生时及时启动应急相应系统撤离至上风口处,并联系当地消防部门灭火。 | ||||
第6部分:泄露应急处理 | ||||
1.泄露后首先启动应急相应系统2.泄露处理前,需穿戴好安全安全防护鞋、穿戴好安全防护手套(强酸性物质需穿戴防酸碱手套)、根据吸入危险性穿戴相应防护面罩。 有关个人防护,请看第8部分。 | ||||
6.2 环境保护措施 | ||||
参照《范德生物化学废弃物处理方法》处理,防止对环境造成危害,处理后交由有资质的废弃物处理结构进行处理,以免造成环境污染。 | ||||
参照《范德生物化学品废弃物处理方法》对泄露的化学品进行处理,处理前需用化学品吸附岩棉对泄露区域进行围挡,形成“围堰”防止泄露扩大。 | ||||
6.4 参考其他部分 | ||||
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。 | ||||
第7部分:操作处置与储存 | ||||
7.1 安全操作的注意事项 | ||||
使用过程请穿戴好口罩,手套等防护用品,避免与皮肤接触、吸入、误食危险。 有关预防措施,请参见章节2.2。 | ||||
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性 | ||||
暂时无法提供详细数据,尽可能避免与其他化合物混合存储,避光、通风处存储。 | ||||
第8部分:接触控制/个体防护 | ||||
8.1 控制参数 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
8.2 暴露控制 | ||||
适当的技术控制 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
个体防护装备 | ||||
一般情况下穿戴安全防护眼镜即可,如有飞溅液体、粉末产生时,请佩戴防溅面罩进行防护。穿戴的防护用品需取得如:GB、NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 等相关认证。 | ||||
手套脱去注意事项:手套在使用前必须进行检查,请使用正确的方法脱除手套(不接触手套外部表面),避免身体任何皮肤部位接触到此产品。根据相关法律法规和实验室管理规范制度,手套使用过后,请将被污染的手套谨慎处理,工作后清洗并吹干双手。 所选择的保护手套必须符合法规《劳动防护用品配备标准》、(EU)2016/425以及从此类法规衍生出来的EN 374标准规范。 完全接触保护要求: 手套材料:丁腈橡胶 手套最小的层厚度:0.11 MM 手套溶剂渗透时间:480 分钟 飞溅保护要求: 材料:丁腈橡胶 最小的层厚度 0.11 MM 溶剂渗透时间:480 分钟 如果以溶剂形式应用或与其它物质混合应用,或在不同于《劳动防护用品配备标准》,EN 374规定的条件下应用,请与EC批准的手套的供应商联系。该条只是作为推荐性建议,如遇特殊情况,务必请熟悉该产品属性的专家,选取相关防护用品。此条建议不应该被认定为适应所有特殊条件防护,请根据所处工作条件请求专业工程师指导采取相应防护措施。 | ||||
选择身体部分的防护措施,需要根据危险物质的类型、浓度、量以及特定的工作环境。身体部分防护设备、防护服的类型,必须根据使用者工作场所中的危险物质的浓度、数量进行选择。 | ||||
一般情况下穿戴普通的医用口罩保护呼吸系统即可。有酸雾产生式活性炭类口罩起不到防护作用,如需对粉尘造成损害进行防护时,请采用N95型(US)或P1型(EN 143)类口罩或者防尘面具。特殊情况下使用自吸式呼吸器时,使用的呼吸器必须对呼吸器密闭性、空气供应系统、供气压进行测试,当然呼吸器需通过强制认证标准如:GB、NIOSH(US)、CEN(EU)。 | ||||
环境暴露的控制 | ||||
不要让产品进入下水道。 | ||||
第9部分:理化特性 | ||||
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息 | ||||
形状:暂无数据 | ||||
颜色:暂无数据 | ||||
气味 | 暂无数据 | |||
气味阈值 | 暂无数据 | |||
暂无数据 | ||||
189-191°C | ||||
初沸点和沸程 | 365.1±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |||
闪点 | 188.8±19.7 °C | |||
蒸发速率 | 暂无数据 | |||
易燃性(固体,气体) | 暂无数据 | |||
高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 | 暂无数据 | |||
蒸气压 | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C | |||
蒸气焓 | 67.1±6.0 kJ/mol | |||
密度/相对密度 | 1.9000 | |||
Soluble in water. Slightly soluble in alcohol and ether. Insoluble in benzene and chloroform. | ||||
正辛醇/水分配系数 | Log Kow (KOWWIN v1.67 estimate) = -1.74/ Boiling Pt, Melting Pt, Vapor Pressure Estimations (MPBPWIN v1.42):
Boiling Pt (deg C): 246.91 (Adapted Stein & Brown method)
Melting Pt (deg C): 62.97 (Mean or Weighted MP)
VP(mm Hg,25 deg C): 0.0056 (Modified Grain method)
MP (exp database): 101.5 deg C
VP (exp database): 2.34E-04 mm Hg at 25 deg C
Subcooled liquid VP: 0.00134 mm Hg (25 deg C, exp database VP ) | |||
正辛醇空气分配系数 | Log Kow used: -1.74 (KowWin est)
Log Kaw used: -8.233 (exp database)
Log Koa (KOAWIN v1.10 estimate): 6.493
Log Koa (experimental database): None | |||
自燃温度 | 暂无数据 | |||
分解温度 | 暂无数据 | |||
黏度 | 暂无数据 | |||
暂无数据 | ||||
氧化性 | 暂无数据 | |||
根据碎片估算水溶胶 | Wat Sol (v1.01 est) = 1e+006 mg/L
Wat Sol (Exper. database match) = 220000.00
Exper. Ref: YALKOWSKY,SH & DANNENFELSER,RM (1992)
Wat Sol (Exper. database match) = 1350.00
Exper. Ref: YALKOWSKY,SH & DANNENFELSER,RM (1992) | |||
亨利定律常数(25摄氏度) | Bond Method : 2.41E-011 atm-m3/mole
Group Method: Incomplete
Exper Database: 1.43E-10 atm-m3/mole
Henrys LC [VP/WSol estimate using EPI values]: 6.635E-010 atm-m3 | |||
9.2 其他安全信息 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第10部分:稳定性和反应性 | ||||
10.1 稳定性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.2 危险反应 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.3 应避免的条件 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.4 禁配物 | ||||
强氧化剂 | ||||
10.5 危险的分解产物 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第11部分:毒理学信息 | ||||
11.1 毒理学影响信息 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
呼吸或皮肤过敏 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
生殖毒性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触) | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
吸入危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
附加说明 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第12部分:生态学危害信息 | ||||
12.1 生态毒性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.2 持久性和降解性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.3 快速生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin1 (Linear Model) : 0.8501
Biowin2 (Non-Linear Model) : 0.9533 | ||||
12.4 专家调查生物降解结果 | ||||
Biowin3 (Ultimate Survey Model): 3.7294 (days-weeks )
Biowin4 (Primary Survey Model) : 4.4890 (hours-days ) | ||||
12.5 MITI生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin5 (MITI Linear Model) : 0.8066
Biowin6 (MITI Non-Linear Model): 0.8999 | ||||
12.6 厌氧生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin7 (Anaerobic Linear Model): 1.2096 | ||||
12.7 现成的生物降解性预测 | ||||
YES | ||||
12.8 碳氢化合物生物降解 | ||||
Structure incompatible with current estimation method! | ||||
12.9 对气溶胶的吸附 | ||||
Vapor pressure (liquid/subcooled): 0.179 Pa (0.00134 mm Hg)
Log Koa (Koawin est ): 6.493
Kp (particle/gas partition coef. (m3/ug)):
Mackay model : 1.68E-005
Octanol/air (Koa) model: 7.64E-007 | ||||
12.10 羟基自由基反应 | ||||
OVERALL OH Rate Constant = 1.0400 E-12 cm3/molecule-sec
Half-Life = 10.285 Days (12-hr day; 1.5E6 OH/cm3) | ||||
12.11 臭氧反应 | ||||
No Ozone Reaction Estimation | ||||
12.12 空气中颗粒物吸附的分数(PHI) | ||||
0.000974 (Junge,Mackay)
Note: the sorbed fraction may be resistant to atmospheric oxidation | ||||
12.13 土壤吸附系数 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.14 碱/酸催化水解(25℃) | ||||
Koc : 1.895
Log Koc: 0.278 / Aqueous Base/Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis (25 deg C) [HYDROWIN v1.67]:
Rate constants can NOT be estimated for this structure!/ | ||||
12.15 利用对数KOW估算生物累积量 | ||||
Log BCF from regression-based method = 0.500 (BCF = 3.162)
log Kow used: -1.74 (estimated) | ||||
12.16 废水处理中的去除 | ||||
Total removal: 1.85 percent
Total biodegradation: 0.09 percent
Total sludge adsorption: 1.75 percent
Total to Air: 0.00 percent
(using 10000 hr Bio P,A,S) | ||||
12.17 三级逸度模型 | ||||
Mass Amount Half-Life Emissions
(percent) (hr) (kg/hr)
Air 0.00504 247 1000
Water 34.5 208 1000
Soil 65.5 416 1000
Sediment 0.0596 1.87e+003 0
Persistence Time: 387 hr | ||||
12.18 土壤中的迁移性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.19 PBT和VPVB的结果评价 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.20 其他环境有害作用 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第13部分:废弃处置 | ||||
13.1 废物处理 | ||||
None | ||||
None | ||||
第14部分:运输信息 | ||||
14.1 联合国编号 / UN NUMBER | ||||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID: | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IMDG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
14.2 联合国运输名称 / UN PROPER SHIPPING NAME | ||||
欧洲陆运危规: | None | |||
国际海运危规: | None | |||
国际空运危规: | None | |||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID: | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IMDG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID : | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IM0DG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
None | ||||
14.6 特殊防范措施 / SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR USER | ||||
None | ||||
None | ||||
第15部分:法律法规信息 | ||||
适用法规 | ||||
《中华人民共和国安全生产法》、《职业病防治法》、《化学化工实验室安全管理规范》 | ||||
其它的规定 | ||||
《生产安全事故报告和调查处理条例》、《职业病防治法》、《职业安全和卫生法》美国1970 | ||||
第16部分:其他补充信息 | ||||
其他信息 版权所有:BIOFOUNT BEIJING BIO TECH CO.,LTD 公司。许可无限制纸张拷贝,仅限于内部使用。 上述信息视为正确,但不包含所有的信息,仅作为指引使用。本文件中的信息是基于我们目前所知,就正确的安全提示来说适用于本品。该信息不代表对此产品性质的保证。BIOFOUNT公司及其附属公司对任何操作或者接触上述产品而引起的损害不负有任何责任。更多使用条款,参见发票或包装条的反面。 更多销售条款及条件请参见HTTP://WWW.BIO-FOUNT.COM/或发票或装箱单的背面。欲悉详情,请联系:SALES@BIO-FOUNT.COM | ||||
- 相关产品
-
< >
- 推荐产品
-
< >
- 最新产品
-
< >
新闻
怎么做细胞爬片免疫组化染色实验
细胞爬片免疫组化染色,是通过细胞爬片是让玻片浸在细胞培养基内,细胞在玻片上生长,主要用于组织学,免疫组织化学...
2020/7/20 22:04:33
提取病毒RNA的实验方法
提取病毒RNA方法分别有:异硫氰酸胍的提取病毒RNA方法、TRIzol LS提取法、Trizol法提取法等等...
2020/7/22 20:29:26

chelex 100树脂国产替代之路-BIOFOUNT范德生物
Chelex 100螯合离子交换树脂对铜、铁和其他重金属?的偏好显著高于对钠、钾等一价阳离子的偏好。它对二价...
2025/11/4 14:22:46

9月开学季——助研新学期 范德送好礼
2025/8/28 15:30:55

Waxfilm 实验室封口膜:技术与国际市场的双重突破
在实验室耗材领域,封口膜是保障实验准确性与稳定性的关键产品之一。近年来,Waxfilm?实验室封口膜凭借其卓...
2025/5/13 13:03:40

Waxfilm实验室封口膜的5大突破
Waxfilm实验室封口膜作为生物功能膜领域的国产技术突破和品牌突破,是生物领域中国技术发展的缩影。
2025/5/6 17:02:07
各种微流控芯片键合方法的优缺点
微流控芯片键合:目前主要有激光焊接、热压键合、胶键合、超音波焊接,每种方法都有各自的优缺点。本文主要介绍聚酯...
2023/7/28 10:43:09

新一代微流控键合解决方案
微流控键合解决方案:微流控芯片制造的一个重要环节,也是最容易被忽视的--芯片键合。其中一个重要因素是:微流控...
2023/7/27 12:44:28
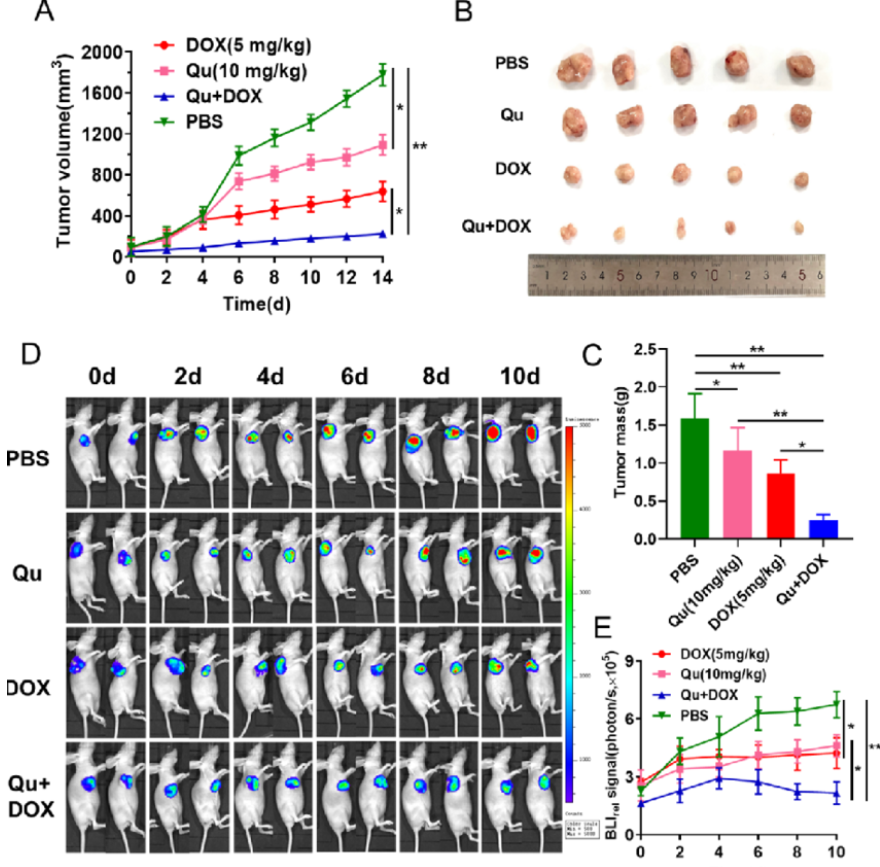
荧光素钾盐使用说明
D-荧光素钾盐(K+)设计用于体外和体内生物发光测定。D-荧光素的质量和纯度对于获得良好和可重复的结果至关重...
2023/7/20 11:05:11
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白)
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白):牛血清白蛋白(BSA)有多种形式,如何选择适合自己的牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是一...
2023/2/14 13:09:18




 购物车
购物车 



