-
肾上腺素
NMR and HPLC COA下载 MSDS下载 - Names:
L-Epinephrine
- CAS号:
51-43-4
MDL Number: MFCD00002204 - MF(分子式): C9H13NO3 MW(分子量): 183.2克/摩尔
- EINECS:200-098-7 Reaxys Number:
- Pubchem ID: Brand:BIOFOUNT
| 货品编码 | 规格 | 纯度 | 价格 (¥) | 现价(¥) | 特价(¥) | 库存描述 | 数量 | 总计 (¥) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YZM006942-500mg | 500mg | >99.0% | ¥ 387.00 | ¥ 387.00 | In-stock | ¥ 0.00 | ||
| YZM003350-500mg | 500mg | >99.5% | ¥ 390.00 | ¥ 390.00 | 2-3天 | ¥ 0.00 | ||
| HCT015780-100mg | 100mg | 97% | ¥ 598.50 | ¥ 598.50 | 4-7周 | ¥ 0.00 |
| 中文别名 | 肾上腺素(51-43-4),4-(1-羟基-2-(甲基氨基)乙基)-1,2-苯二醇;醋酸肾上腺素;肾上腺素酒石酸;盐酸肾上腺素;表蛋白;盐酸肾上腺素;肾上腺素酒石酸氢盐;溶蛋白;Medihaler-Epi; |
| 英文别名 | L-Epinephrine(51-43-4);4-(1-Hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl)-1,2-benzenediol;Acetate, Epinephrine;Adrenaline;Adrenaline Acid Tartrate;Adrenaline Bitartrate;Adrenaline Hydrochloride;Epifrin;Epinephrine;Epinephrine Acetate;Epinephrine Bitartrate;Epinephrine Hydrochloride;Epinephrine Hydrogen Tartrate;Epitrate;Lyophrin;Medihaler-Epi; |
| CAS号 | 51-43-4 |
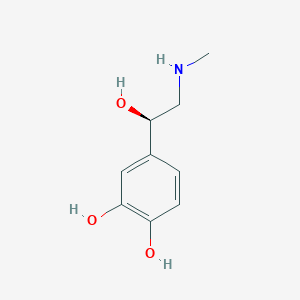
| SMILES | O[C@H](C1=CC(O)=C(O)C=C1)CNC |
| Inchi | InChI=1S/C9H13NO3/c1-10-5-9(13)6-2-3-7(11)8(12)4-6/h2-4,9-13H,5H2,1H3/t9-/m0/s1 |
| InchiKey | UCTWMZQNUQWSLP-VIFPVBQESA-N |
| 分子式 Molecular Weight | C9H13NO3 |
| 分子量 Formula | 183.2克/摩尔 |
| 闪点 FP | 207.9±17.9 °C |
| 熔点 Melting point | 211-212℃ |
| 沸点 Boiling point | 413.1±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Polarizability极化度 | 19.6±0.5 10-24cm3 |
| 密度 Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| 蒸汽压 Vapor Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| 溶解度Solubility | 几乎不溶于水,乙醇(96%)和二氯甲烷。 溶于盐酸。 |
| 性状 | 白色至接近白色的微晶粉末或颗粒 |
| 储藏条件 Storage conditions | 2-8°C,库房低温,通风,干燥,与食品原料分开存放 |
肾上腺素(51-43-4,L-Epinephrine)毒理性质:
| 生物 | 测试类型 | 路线 | 剂量 | 影响 | 参考 |
| man | TDLo | oral | 77 mg/kg (77 mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: HALLUCINATIONS, DISTORTED PERCEPTIONS; BEHAVIORAL: EXCITEMENT; GASTROINTESTINAL: NAUSEA OR VOMITING | Annals of Emergency Medicine., 19(671), 1990 [PMID:1971502] |
| man | TDLo | subcutaneous | 43 ug/kg (0.043 mg/kg) | CARDIAC: PULSE RATE INCREASE WITHOUT FALL IN BP; GASTROINTESTINAL: NAUSEA OR VOMITING; SKIN AND APPENDAGES (SKIN): SWEATING: OTHER | Annals of Emergency Medicine., 19(680), 1990 [PMID:2344087] |
| man | LDLo | subcutaneous | 7 ug/kg (0.007 mg/kg) | BRAIN AND COVERINGS: OTHER DEGENERATIVE CHANGES; CARDIAC: OTHER CHANGES | Annals of Emergency Medicine., 28(725), 1996 [PMID:8953972] |
| man | TDLo | subcutaneous | 8571 ng/kg/80M (0.008571 mg/kg) | CARDIAC: CARDIOMYOPATHY INCLUDING INFARCTION | American Heart Journal., 111(1193), 1986 [PMID:2940853] |
| women | TDLo | intravenous | 6 ug/kg (0.006 mg/kg) | CARDIAC: ARRHYTHMIAS (INCLUDING CHANGES IN CONDUCTION) | British Medical Journal., 286(519), 1983 |
| man | TDLo | intravenous | 285 ug/kg (0.28499999999999998 mg/kg) | CARDIAC: EKG CHANGES NOT DIAGNOSTIC OF ABOVE | American Journal of Emergency Medicine., 7(485), 1989 [PMID:2757714] |
| man | TDLo | intravenous | 3 mg/kg (3 mg/kg) | VASCULAR: CONTRACTION (ISOLATED TISSUES) | American Journal of Emergency Medicine., 8(46), 1990 [PMID:2293835] |
| man | TDLo | intramuscular | 2 ug/kg (0.002 mg/kg) | VASCULAR: REGIONAL OR GENERAL ARTERIOLAR CONSTRICTION | American Journal of Emergency Medicine., 8(46), 1990 [PMID:2293835] |
| man | TDLo | intravenous | 16 ug/kg (0.016 mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: HALLUCINATIONS, DISTORTED PERCEPTIONS; CARDIAC: CHANGE IN RATE; VASCULAR: BP LOWERING NOT CHARACTERIZED IN AUTONOMIC SECTION | American Journal of Emergency Medicine., 5(64), 1987 [PMID:3814285] |
| infant | TDLo | multiple routes | 625 ug/kg/I (0.625 mg/kg) | CARDIAC: PULSE RATE INCREASE WITHOUT FALL IN BP; LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: CYANOSIS; KIDNEY, URETER, AND BLADDER: CHANGES IN TUBULES (INCLUDING ACUTE RENAL FAILURE, ACUTE TUBULAR NECROSIS) | Southern Medical Journal., 78(874), 1985 [PMID:4012388] |
| rat | LDLo | oral | 30 mg/kg (30 mg/kg) | Structure et Activite Pharmacodyanmique des Medicaments du Systeme Nerveux Vegetatif, Bovet, D., and F. Bovet-Nitti, New York, S. Karger, 1948, -(22), 1948 | |
| rat | LD50 | skin | 62 mg/kg (62 mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: SOMNOLENCE (GENERAL DEPRESSED ACTIVITY); BEHAVIORAL: CONVULSIONS OR EFFECT ON SEIZURE THRESHOLD; BEHAVIORAL: EXCITEMENT | Gigiena Truda i Professional'nye Zabolevaniya. Labor Hygiene and Occupational Diseases., 8(4)(30), 1964 |
| rat | LDLo | intraperitoneal | 10 mg/kg (10 mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: CONVULSIONS OR EFFECT ON SEIZURE THRESHOLD; BEHAVIORAL: MUSCLE WEAKNESS; LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: DYSPNEA | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics., 88(268), 1946 |
| rat | LD50 | subcutaneous | 5 mg/kg (5 mg/kg) | LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: RESPIRATORY STIMULATION | Schweizerische Medizinische Wochenschrift., 71(554), 1941 |
| rat | LD50 | intravenous | 150 ug/kg (0.15 mg/kg) | Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie., 41(365), 1931 | |
| rat | LD50 | intramuscular | 3500 mg/kg (3500 mg/kg) | Drug Dosages in Laboratory Animals - A Handbook, Rev. ed., Barnes, C.D., and L.G. Eltherington, Berkeley, Univ. of California Press, 1973, -(105), 1973 | |
| mouse | LDLo | oral | 50 mg/kg (50 mg/kg) | Structure et Activite Pharmacodyanmique des Medicaments du Systeme Nerveux Vegetatif, Bovet, D., and F. Bovet-Nitti, New York, S. Karger, 1948, -(22), 1948 | |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 4 mg/kg (4 mg/kg) | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics., 90(110), 1947 | |
| mouse | LD50 | subcutaneous | 1470 ug/kg (1.47 mg/kg) | Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archiv fuer Experimentelle Pathologie und Pharmakologie., 202(658), 1943 | |
| mouse | LDLo | unreported | 10 mg/kg (10 mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: CONVULSIONS OR EFFECT ON SEIZURE THRESHOLD; BEHAVIORAL: EXCITEMENT; LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: DYSPNEA | Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archiv fuer Experimentelle Pathologie und Pharmakologie., 162(46), 1931 |
| dog | LD50 | subcutaneous | 5 mg/kg (5 mg/kg) | Drugs in Japan, 6(120), 1982 | |
| dog | LD50 | intravenous | 100 ug/kg (0.1 mg/kg) | Drugs in Japan, 6(120), 1982 | |
| dog | LDLo | parenteral | 5 ug/kg (0.005 mg/kg) | CARDIAC: ARRHYTHMIAS (INCLUDING CHANGES IN CONDUCTION) | Pharmacology: International Journal of Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology., 1(189), 1968 [PMID:5676239] |
| cat | LDLo | subcutaneous | 20 mg/kg (20 mg/kg) | Structure et Activite Pharmacodyanmique des Medicaments du Systeme Nerveux Vegetatif, Bovet, D., and F. Bovet-Nitti, New York, S. Karger, 1948, -(22), 1948 | |
| cat | LDLo | intravenous | 500 ug/kg (0.5 mg/kg) | Structure et Activite Pharmacodyanmique des Medicaments du Systeme Nerveux Vegetatif, Bovet, D., and F. Bovet-Nitti, New York, S. Karger, 1948, -(22), 1948 | |
| rabbit | LD50 | subcutaneous | 4 mg/kg (4 mg/kg) | LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: RESPIRATORY STIMULATION | Schweizerische Medizinische Wochenschrift., 71(554), 1941 |
| rabbit | LD50 | intravenous | 50 ug/kg (0.05 mg/kg) | LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: RESPIRATORY STIMULATION | Schweizerische Medizinische Wochenschrift., 71(554), 1941 |
| guinea pig | LDLo | subcutaneous | 800 ug/kg (0.8 mg/kg) | Structure et Activite Pharmacodyanmique des Medicaments du Systeme Nerveux Vegetatif, Bovet, D., and F. Bovet-Nitti, New York, S. Karger, 1948, -(22), 1948 | |
| guinea pig | LDLo | intravenous | 100 ug/kg (0.1 mg/kg) | Structure et Activite Pharmacodyanmique des Medicaments du Systeme Nerveux Vegetatif, Bovet, D., and F. Bovet-Nitti, New York, S. Karger, 1948, -(22), 1948 | |
| mouse | LD50 | intravenous | 217 ug/kg (0.217 mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: CHANGES IN MOTOR ACTIVITY (SPECIFIC ASSAY); CARDIAC: PULSE RATE INCREASE WITHOUT FALL IN BP; SKIN AND APPENDAGES (SKIN): HAIR: OTHER | Acta Pharmacologica et Toxicologica., 38(474), 1976 [PMID:989250] |
| rabbit | LDLo | oral | 30 mg/kg (30 mg/kg) | Structure et Activite Pharmacodyanmique des Medicaments du Systeme Nerveux Vegetatif, Bovet, D., and F. Bovet-Nitti, New York, S. Karger, 1948, -(22), 1948 |
肾上腺素(51-43-4,L-Epinephrine)实验注意事项:
1.实验前需戴好防护眼镜,穿戴防护服和口罩,佩戴手套,避免与皮肤接触。
2.实验过程中如遇到有毒或者刺激性物质及有害物质产生,必要时实验操作需要手套箱内完成以免对实验人员造成伤害
3.实验后产生的废弃物需分类存储,并交于专业生物废气物处理公司处理,以免造成环境污染Experimental considerations:
1. Wear protective glasses, protective clothing and masks, gloves, and avoid contact with the skin during the experiment.
2. The waste generated after the experiment needs to be stored separately, and handed over to a professional biological waste gas treatment company to avoid environmental pollution.
Tags:肾上腺素试剂,肾上腺素合成,肾上腺素杂质,肾上腺素中间体,肾上腺素闪点,肾上腺素旋光度,肾上腺素溶解度,肾上腺素结构式,肾上腺素购买,肾上腺素MSDS,
| 产品说明 | 肾上腺素(51-43-4)是由肾上腺髓质分泌的激素,肾上腺素来源于氨基酸苯丙氨酸和酪氨酸.肾上腺素溶解度,肾上腺素MSDS,肾上腺素结构式详见主页 |
| Introduction | 肾上腺素(51-43-4,L-Epinephrine) is a hormone secreted by the medulla of the adrenal glands. L-Epinephrine is anα-adrenergicandβ-adrenergicreceptor agonist. |
| Application1 | 肾上腺素是儿茶酚胺,一种拟交感神经的单胺,来源于氨基酸苯丙氨酸和酪氨酸。它是大多数物种从肾上腺髓质分泌的活性拟交感神经激素。 |
| Application2 | |
| Application3 |
肾上腺素(51-43-4,L-Epinephrine)药理学:
※肾上腺素为白色至接近白色的微晶粉末或颗粒。无臭。熔点211-212℃。水溶液是弱碱性的。略带苦味,麻木。
※肾上腺素是天然的拟交感神经胺的合成形式,具有收缩血管,降低眼内压和扩张支气管的活性。通过刺激血管α-肾上腺素受体,肾上腺素引起血管收缩,从而增加血管抵抗力和血压。当在结膜中给药时,该药物与虹膜括约肌中的α-肾上腺素受体结合,导致血管收缩,房水产生减少和眼内压降低。肾上腺素通过其beta1受体刺激作用,增加了心肌收缩的力量和速率,并放松了支气管平滑肌,导致支气管扩张。
肾上腺素是儿茶酚胺,一种拟交感神经的单胺,来源于氨基酸苯丙氨酸和酪氨酸。它是大多数物种从肾上腺髓质分泌的活性拟交感神经激素。它同时刺激α和β肾上腺素能系统,引起全身血管收缩和胃肠道松弛,刺激心脏,并扩张支气管和脑血管。它用于哮喘和心力衰竭,并延迟局部麻醉药的吸收。肾上腺素还可以扩张皮肤和肠道的小动脉,同时扩张腿部肌肉的小动脉。通过增加糖原水解成葡萄糖的方式来提高血糖水平在肝脏中,同时开始分解脂肪细胞中的脂质。肾上腺素对免疫系统具有抑制作用。
※肾上腺素来自肾上腺髓质的活性拟交感神经激素。 它刺激α-和β-肾上腺素能系统,引起全身血管舒张和胃肠道松弛,刺激心脏,并扩张支气管和脑血管。 它用于哮喘和心脏衰竭,并延迟局部麻醉药的吸收。
※Epinephrine, also known as adrenaline or epipen, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as catechols. Catechols are compounds containing a 1, 2-benzenediol moiety. Epinephrine is a drug which is used to treat anaphylaxis and sepsis. also one of the body's main adrenergic neurotransmitters. Epinephrine exists as a solid, soluble (in water), and a very weakly acidic compound (based on its pKa). Epinephrine has been found throughout most human tissues, and has also been detected in multiple biofluids, such as urine, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid. Within the cell, epinephrine is primarily located in the cytoplasm and myelin sheath. Epinephrine participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, S-Adenosylhomocysteine and epinephrine can be biosynthesized from S-adenosylmethionine and norepinephrine; which is catalyzed by the enzyme phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase. Furthermore, Epinephrine can be converted into 3, 4-dihydroxymandelaldehyde and methylamine; which is mediated by the enzyme amine oxidase [flavin-containing] a. Finally, S-Adenosylhomocysteine and epinephrine can be biosynthesized from S-adenosylmethionine and norepinephrine; which is mediated by the enzyme phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase. In humans, epinephrine is involved in the disulfiram action pathway, the epinephrine action pathway, the tyrosine metabolism pathway, and catecholamine biosynthesis pathway. Epinephrine is also involved in several metabolic disorders, some of which include the alkaptonuria pathway, tyrosinemia, transient, OF the newborn pathway, the tyrosinemia type I pathway, and aromatic L-aminoacid decarboxylase deficiency.
※The active sympathomimetic hormone from the ADRENAL MEDULLA. It stimulates both the alpha- and beta- adrenergic systems, causes systemic VASOCONSTRICTION and gastrointestinal relaxation, stimulates the HEART, and dilates BRONCHI and cerebral vessels. It is used in ASTHMA and CARDIAC FAILURE and to delay absorption of local ANESTHETICS.
肾上腺素(51-43-4,L-Epinephrine)物理属性:
| 物理特性 | 值 | 单位 | 温度(摄氏度) | 资源 |
| Melting Point | 211.5 | deg C | EXP | |
| pKa Dissociation Constant | 8.59 | (none) | 25 | EXP |
| log P (octanol-water) | -1.37E+00 | (none) | EXP | |
| Water Solubility | 180 | mg/L | 20 | EXP |
| Vapor Pressure | 7.37E-07 | mm Hg | 25 | EST |
| Henry's Law Constant | 7.06E-19 | atm-m3/mole | 25 | EST |
| Atmospheric OH Rate Constant | 1.38E-10 | cm3/molecule-sec | 25 | EST |
| 警示图 | |
| 危险性 | warning |
| 危险性警示 | Not available |
| 安全声明 | H303吞入可能有害+H313皮肤接触可能有害+H2413吸入可能对身体有害 |
| 安全防护 | P264处理后彻底清洗+P280戴防护手套/穿防护服/戴防护眼罩/戴防护面具+P305如果进入眼睛+P351用水小心冲洗几分钟+P338取出隐形眼镜(如果有)并且易于操作,继续冲洗+P337如果眼睛刺激持续+P2393获得医疗建议/护理 |
| 备注 | 实验过程中防止吸入、食入,做好安全防护 |
肾上腺素(51-43-4,L-Epinephrine)危害标识:
| 象形图 |  |
| 信号 | Danger |
| GHS危险说明 | Aggregated GHS information provided by 100 companies from 7 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. |
| H301 (97%): Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] | |
| H310 (96%): Fatal in contact with skin [Danger Acute toxicity, dermal] | |
| H331 (93%): Toxic if inhaled [Danger Acute toxicity, inhalation] | |
| Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. | |
| 防范说明代码 | P261, P262, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P310, P302+P350, P304+P340, P310, P311, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P403+P233, P405, and P501 |
| (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| .Alm A, et al. The effect of topical l-epinephrine on regional ocular blood flow in monkeys. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1980 May;19(5):487-91. |
| .Simons FE, et al. First-aid treatment of anaphylaxis to food: focus on epinephrine. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004 May;113(5):837-44. |
| Morris KA, et al. Epinephrine and glucose modulate training-related CREB phosphorylation in old rats: relationships to age-related memory impairments. Exp Gerontol. 2013 Feb;48(2):115-27. |
| Callaway CW, et al. Epinephrine for cardiac arrest. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2013 Jan;28(1):36-42. |
| Bennett MR: One hundred years of adrenaline: the discovery of autoreceptors. Clin Auton Res. 1999 Jun;9(3):145-59. [PMID:10454061] |
肾上腺素(51-43-4,L-Epinephrine)参考文献:
1、The Disparate Effects of Epinephrine and Norepinephrine on Hyperglycemia in Cardiovascular Surgery
Daniel Phadke , Jared P Beller , Curt Tribble
Abstract:Hyperglycemia is a metabolic derangement that frequently develops after cardiovascular surgery. The perioperative administration of inotropic and vasoactive agents, such as epinephrine and norepinephrine, are common in the management of cardiac surgery patients and are known to contribute to the development of postoperative hyperglycemia. We hypothesized that hemodynamic support with epinephrine exacerbates postoperative hyperglycemia to a greater degree than does treatment with norepinephrine. This literature review outlines the mechanisms by which epinephrine and norepinephrine alter glucose homeostasis, while highlighting the significant differences in their effects on hepatic glucose mobilization and peripheral glucose utilization. This review suggests that the use of epinephrine exacerbates postoperative hyperglycemia to a greater degree than does norepinephrine.
2、The Epinephrine/Norepinephrine/Autoinducer-3 Interkingdom Signaling System in Escherichia coli O157:H7
Cristiano G Moreira , Vanessa Sperandio
Abstract:Epinephrine/norepinephrine/AI-3 signaling is used as an interkingdom chemical signaling system between microbes and their hosts. This system is also exploited by pathogens to regulate virulence traits. In enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) O157:H7, it is essential for pathogenesis and flagella motility. These three signals activate expression of a pathogenicity island named locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE), Shiga toxin, and the flagella regulon. These signals are sensed by the two-component system QseBC, whereas the bacterial membrane receptor QseC autophosphorylates and phosphorylates the QseB response regulator initiating a complex phosphorelay signaling cascade that activates the expression of a second two-component system, QseEF. The QseEF two-component system is also involved in the expression of the virulence genes, and it senses epinephrine, phosphate, and sulfate. This complex signaling cascade still needs to be completely elucidated.
3、Stress hormone epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) effects on the anaerobic bacteria
Lyudmila Boyanova
Abstract:Microbial endocrinology is a relatively new research area that already encompasses the anaerobes. Stress hormones, epinephrine and norepinephrine, can affect the growth of anaerobic bacteria such as Fusobacterium nucleatum, Prevotella spp., Porhyromonas spp., Tanerella forsythia and Propionibacterium acnes and can increase virulence gene expression, iron acquisition and many virulence factors of some anaerobic species such as Clostridium perfringens, Porphyromonas gingivalis and Brachyspira pilosicoli. Epinephrine and norepinephrine effects can lead to a growth increase or decrease, or no effect on the growth of the anaerobes. The effects are species-specific and perhaps strain-specific. Discrepancies in the results of some studies can be due to the different methods and media used, catecholamine concentrations, measurement techniques and the low number of strains tested. Biological effects of the stress hormones on the anaerobes may range from halitosis and a worsening of periodontal diseases to tissue damages and atherosclerotic plaque ruptures. Optimizations of the research methods and a detailed assessment of the catecholamine effects in conditions mimicking those in affected organs and tissues, as well as the effects on the quorum sensing and virulence of the anaerobes and the full spectrum of biological consequences of the effects are interesting topics for further evaluation.
4、Epinephrine-Induced Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy During Laparoscopic Myomectomy: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Joseph Nassif , Hasan Nahouli , Ali Khalil , Elie Mikhael, Walid Gharzeddine , Ghina Ghaziri
Abstract:Laparoscopic myomectomy, a minimally invasive procedure performed for the management of uterine leiomyomas, involves a challenging aspect: excessive local bleeding. Hemorrhage control during laparoscopic myomectomy can be achieved through the use of a wide range of vasoconstrictors, including epinephrine. Epinephrine is frequently used for the control of local bleeding during surgery; however, it has been associated with several complications. In this case report, we present a rare and unique case of stress-induced cardiomyopathy, also known as Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (TC), caused by intramyomal injection of epinephrine during laparoscopic myomectomy. TC is a transient type of cardiomyopathy associated with a reversible regional systolic and diastolic dysfunction of the left ventricle as well as various abnormal wall motions, and is often indistinguishable from myocardial infarction. TC is more prevalent in women than in men and has been linked to supraphysiological levels of plasma catecholamine. Although epinephrine is an effective vasoconstrictor used to control bleeding, it is potentially associated with adverse events that should be thoroughly investigated within the field of gynecology and its application to laparoscopic myomectomy.
5、Stable Parent Anions of Dopamine and Adrenaline: A New Form of Neurotransmitters
Chu Gong , Wei Wang , Kit Bowen , Xinxing Zhang
Abstract:Previously, dopamine and adrenaline were only known to exist in three closed-shell forms: neutral molecules (including zwitterions), protonated cations, and deprotonated anions. In the present work, stable open-shell parent anions of dopamine and adrenaline were generated in the gas phase and characterized by a combination of anion photoelectron spectroscopy and calculations. These anions were formed as a result of an enol-keto-type tautomerization initiated by the attachment of excess electrons. Calculations showed that hydrogen atoms on the hydroxyl groups of dopamine and adrenaline migrated to adjacent carbon atoms under the influence of the additional electron, breaking the aromaticity of the benzene ring and resulting in the formation of the rare anionic tautomers. We speculate that the secondary electrons generated in scenarios such as radiotherapy could produce the anions reported in this work, providing a potential new depletion channel of these molecules in vivo.
化学品安全技术说明书 | 版本:1.0 | |||
按照GB/T16483、GB/T17519编制 | 修订日期:10.07.2019 | |||
| 打印日期:19.02.2020 | |||
版权所有:范德(北京)生物科技有限责任公司 | 最初编制日期:25.05.2017 | |||
公司网站:WWW.BIO-FOUNT.COM | SDS编号:YZM003350 | |||
版权所有:BIOFOUNT BEIJING BIO TECH CO.,LTD | 产品编号:YZM003350 | |||
L-Epinephrine | ||||
说明书目录 | ||||
第1部分 | 第2部分 | 危险性概述 | ||
第3部分 | 成分/组成信息 | 第4部分 | 急救措施 | |
第5部分 | 消防措施 | 第6部分 | 泄露应急处理 | |
第7部分 | 操作处置与储存 | 第8部分 | 接触控制/个体防护 | |
第9部分 | 理化性质 | 第10部分 | 稳定性和反应性 | |
第11部分 | 毒理学信息 | 第12部分 | 生态学危害信息 | |
第13部分 | 废弃处置 | 第14部分 | 运输信息 | |
第15部分 | 法律法规信息 | 第16部分 | 其他补充信息 | |
第1部分:化学品及企业标识 | ||||
1.1 产品标识 | ||||
L-Epinephrine | ||||
ENGLISH NAME: | L-Epinephrine | |||
YZM003350 | ||||
BIOFOUNT | ||||
51-43-4 | ||||
1.2 安全技术说明书提供者的详情 | ||||
制造商或供应商名称: | ||||
制造地址: | 59 KANGTAI AVENUE BINHAI NEW DISTRICT TIANJIN 300450 TIANJIN CHINA 范德(天津)生物科技有限责任公司 天津市滨海新区康泰大道59号九州通绿谷健康产业园 邮政编码:300450 | |||
电话号码: | | |||
1.3 应急咨询电话 | ||||
紧急联系电话: | | |||
1.4 物质或混合物的推荐用途和限制用途 | ||||
已确认的各用途: | 仅用于科学研发,不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。 | |||
第2部分:危险性概述 | ||||
2.1 GHS危险性类别 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.2 GHS 标签要素,包括防范说明 | ||||
象形图 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
H301,H310 | ||||
警告申明 | ||||
P261,P280,P310 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
事故响应 | ||||
1.化学品使用过程中,当出现事故或者有紧急情况发生时,当事人应第一时间向应急小组负责人汇报后,由应急小组采取措施防止事态扩大。2.应急小组对受害人采取救护措施。 | ||||
4°C, protect from light, stored under nitrogen * 该产品在溶液状态不稳定,建议您现用现配,即刻使用。 | ||||
废弃处置 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.3 物理和化学危险 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.4 健康危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.5 环境危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
2.6 其它危害物 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第3部分:成分/组成信息 | ||||
物质/混合物 | 暂无数据 | |||
3.1 物 质 | ||||
C9H13NO3 | ||||
183.2 | ||||
51-43-4 | ||||
EC-编号 | 暂无数据 | |||
根据相应法规,无需披露具体组份。 | ||||
第4部分:急救措施 | ||||
4.1 必要的急救措施描述 | ||||
吸入 | ||||
立即将患者移至空气新鲜处,发现呼吸困难时,必须立即采取吸氧处理,停止呼吸时采取人工呼吸。同时联系及时就医。 | ||||
皮肤接触 | ||||
立即脱去或者剪去污染的衣物,迅速用大量的流动清水冲10-20分钟甚至更长时间后,赴医院就医。 | ||||
眼睛接触 | ||||
立即用大量的流动清水冲10-20分钟后赴医院就医处理。 | ||||
食入 | ||||
误食化学物品后,应立即采取措施进行催吐。1.若误食化学品呈酸性,则可服用大量牛奶和水,促使食如折呕吐。2.若误食化学品呈碱性,则可服用大量牛奶、清水和醋,促使其呕吐,紧急处理后,应及时送至医院进行治疗(仅供参考)。食如者昏迷状态下禁止催吐,以免造成窒息。 | ||||
4.2 最重要的症状和健康影响 | ||||
最重要的已知症状及作用已在标签(参见章节2.2)和/或章节11中介绍 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
4.4 对医生的特别提示 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第5部分:消防措施 | ||||
5.1 灭火介质 | ||||
采用泡沫灭火器、二氧化碳灭火器,避免造成二次污染发生。 | ||||
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
5.3 灭火注意事项及保护措施 | ||||
小规模着火需戴好口罩,防止有毒气体吸入。火灾发生时及时启动应急相应系统撤离至上风口处,并联系当地消防部门灭火。 | ||||
第6部分:泄露应急处理 | ||||
1.泄露后首先启动应急相应系统2.泄露处理前,需穿戴好安全安全防护鞋、穿戴好安全防护手套(强酸性物质需穿戴防酸碱手套)、根据吸入危险性穿戴相应防护面罩。 有关个人防护,请看第8部分。 | ||||
6.2 环境保护措施 | ||||
参照《范德生物化学废弃物处理方法》处理,防止对环境造成危害,处理后交由有资质的废弃物处理结构进行处理,以免造成环境污染。 | ||||
参照《范德生物化学品废弃物处理方法》对泄露的化学品进行处理,处理前需用化学品吸附岩棉对泄露区域进行围挡,形成“围堰”防止泄露扩大。 | ||||
6.4 参考其他部分 | ||||
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。 | ||||
第7部分:操作处置与储存 | ||||
7.1 安全操作的注意事项 | ||||
使用过程请穿戴好口罩,手套等防护用品,避免与皮肤接触、吸入、误食危险。 有关预防措施,请参见章节2.2。 | ||||
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性 | ||||
暂时无法提供详细数据,尽可能避免与其他化合物混合存储,避光、通风处存储。 | ||||
第8部分:接触控制/个体防护 | ||||
8.1 控制参数 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
8.2 暴露控制 | ||||
适当的技术控制 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
个体防护装备 | ||||
一般情况下穿戴安全防护眼镜即可,如有飞溅液体、粉末产生时,请佩戴防溅面罩进行防护。穿戴的防护用品需取得如:GB、NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 等相关认证。 | ||||
手套脱去注意事项:手套在使用前必须进行检查,请使用正确的方法脱除手套(不接触手套外部表面),避免身体任何皮肤部位接触到此产品。根据相关法律法规和实验室管理规范制度,手套使用过后,请将被污染的手套谨慎处理,工作后清洗并吹干双手。 所选择的保护手套必须符合法规《劳动防护用品配备标准》、(EU)2016/425以及从此类法规衍生出来的EN 374标准规范。 完全接触保护要求: 手套材料:丁腈橡胶 手套最小的层厚度:0.11 MM 手套溶剂渗透时间:480 分钟 飞溅保护要求: 材料:丁腈橡胶 最小的层厚度 0.11 MM 溶剂渗透时间:480 分钟 如果以溶剂形式应用或与其它物质混合应用,或在不同于《劳动防护用品配备标准》,EN 374规定的条件下应用,请与EC批准的手套的供应商联系。该条只是作为推荐性建议,如遇特殊情况,务必请熟悉该产品属性的专家,选取相关防护用品。此条建议不应该被认定为适应所有特殊条件防护,请根据所处工作条件请求专业工程师指导采取相应防护措施。 | ||||
选择身体部分的防护措施,需要根据危险物质的类型、浓度、量以及特定的工作环境。身体部分防护设备、防护服的类型,必须根据使用者工作场所中的危险物质的浓度、数量进行选择。 | ||||
一般情况下穿戴普通的医用口罩保护呼吸系统即可。有酸雾产生式活性炭类口罩起不到防护作用,如需对粉尘造成损害进行防护时,请采用N95型(US)或P1型(EN 143)类口罩或者防尘面具。特殊情况下使用自吸式呼吸器时,使用的呼吸器必须对呼吸器密闭性、空气供应系统、供气压进行测试,当然呼吸器需通过强制认证标准如:GB、NIOSH(US)、CEN(EU)。 | ||||
环境暴露的控制 | ||||
不要让产品进入下水道。 | ||||
第9部分:理化特性 | ||||
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息 | ||||
形状:暂无数据 | ||||
| 颜色:暂无数据 | |||
气味 | 暂无数据 | |||
气味阈值 | 暂无数据 | |||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
初沸点和沸程 | 413.1±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |||
闪点 | 207.9±17.9 °C | |||
蒸发速率 | 暂无数据 | |||
易燃性(固体,气体) | 暂无数据 | |||
高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 | 暂无数据 | |||
蒸气压 | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C | |||
蒸气焓 | 70.2±3.0 kJ/mol | |||
密度/相对密度 | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | |||
DMSO 40 mg/mlMedChem ExpressHY-B0447BDMSO:<7mg/mlMedChem ExpressHY-B0447B | ||||
正辛醇/水分配系数 | Log Kow (KOWWIN v1.67 estimate) = -0.69
Log Kow (Exper. database match) = -1.37
Exper. Ref: Hansch,C & Leo,A (1985)/ Boiling Pt, Melting Pt, Vapor Pressure Estimations (MPBPWIN v1.42):
Boiling Pt (deg C): 345.38 (Adapted Stein & Brown method)
Melting Pt (deg C): 123.68 (Mean or Weighted MP)
VP(mm Hg,25 deg C): 7.48E-008 (Modified Grain method)
MP (exp database): 211-212 deg C
Subcooled liquid VP: 7.07E-006 mm Hg (25 deg C, Mod-Grain method) | |||
正辛醇空气分配系数 | Log Kow used: -1.37 (exp database)
Log Kaw used: -16.540 (HenryWin est)
Log Koa (KOAWIN v1.10 estimate): 15.170
Log Koa (experimental database): None | |||
自燃温度 | 暂无数据 | |||
分解温度 | 暂无数据 | |||
黏度 | 暂无数据 | |||
暂无数据 | ||||
氧化性 | 暂无数据 | |||
根据碎片估算水溶胶 | Wat Sol (v1.01 est) = 1e+006 mg/L
Wat Sol (Exper. database match) = 180.00
Exper. Ref: YALKOWSKY,SH & DANNENFELSER,RM (1992) | |||
亨利定律常数(25摄氏度) | Bond Method : 7.06E-019 atm-m3/mole
Group Method: Incomplete
Henrys LC [VP/WSol estimate using EPI values]: 1.803E-014 atm-m3/mole | |||
9.2 其他安全信息 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第10部分:稳定性和反应性 | ||||
10.1 稳定性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.2 危险反应 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.3 应避免的条件 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
10.4 禁配物 | ||||
强氧化剂 | ||||
10.5 危险的分解产物 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第11部分:毒理学信息 | ||||
11.1 毒理学影响信息 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
呼吸或皮肤过敏 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
生殖毒性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触) | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
吸入危害 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
附加说明 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第12部分:生态学危害信息 | ||||
12.1 生态毒性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.2 持久性和降解性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.3 快速生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin1 (Linear Model) : 1.2045
Biowin2 (Non-Linear Model) : 0.9885
Expert Survey Biodegradation Results:
Biowin3 (Ultimate Survey Model): 3.0915 (weeks )
Biowin4 (Primary Survey Model) : 3.8355 (days ) | ||||
12.4 专家调查生物降解结果 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.5 MITI生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin5 (MITI Linear Model) : 0.5547
Biowin6 (MITI Non-Linear Model): 0.5012 | ||||
12.6 厌氧生物降解的可能性 | ||||
Biowin7 (Anaerobic Linear Model): 1.0008 | ||||
12.7 现成的生物降解性预测 | ||||
YES | ||||
12.8 碳氢化合物生物降解 | ||||
Structure incompatible with current estimation method! | ||||
12.9 对气溶胶的吸附 | ||||
Vapor pressure (liquid/subcooled): 0.000943 Pa (7.07E-006 mm Hg)
Log Koa (Koawin est ): 15.170
Kp (particle/gas partition coef. (m3/ug)):
Mackay model : 0.00318
Octanol/air (Koa) model: 363 | ||||
12.10 羟基自由基反应 | ||||
OVERALL OH Rate Constant = 138.1532 E-12 cm3/molecule-sec
Half-Life = 0.077 Days (12-hr day; 1.5E6 OH/cm3)
Half-Life = 0.929 Hrs | ||||
12.11 臭氧反应 | ||||
No Ozone Reaction Estimation
Reaction With Nitrate Radicals May Be Important! | ||||
12.12 空气中颗粒物吸附的分数(PHI) | ||||
0.153 (Junge,Mackay)
Note: the sorbed fraction may be resistant to atmospheric oxidation | ||||
12.13 土壤吸附系数 | ||||
Koc : 133.1
Log Koc: 2.124 | ||||
12.14 碱/酸催化水解(25℃) | ||||
Rate constants can NOT be estimated for this structure! | ||||
12.15 利用对数KOW估算生物累积量 | ||||
Log BCF from regression-based method = 0.500 (BCF = 3.162)
log Kow used: -1.37 (expkow database) | ||||
12.16 废水处理中的去除 | ||||
Total removal: 1.85 percent
Total biodegradation: 0.09 percent
Total sludge adsorption: 1.75 percent
Total to Air: 0.00 percent
(using 10000 hr Bio P,A,S) | ||||
12.17 三级逸度模型 | ||||
Mass Amount Half-Life Emissions
(percent) (hr) (kg/hr)
Air 3.78e-011 1.86 1000
Water 39 360 1000
Soil 60.9 720 1000
Sediment 0.0713 3.24e+003 0
Persistence Time: 579 hr | ||||
12.18 土壤中的迁移性 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.19 PBT和VPVB的结果评价 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
12.20 其他环境有害作用 | ||||
暂无数据 | ||||
第13部分:废弃处置 | ||||
13.1 废物处理 | ||||
None | ||||
None | ||||
第14部分:运输信息 | ||||
14.1 联合国编号 / UN NUMBER | ||||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID: | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IMDG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
14.2 联合国运输名称 / UN PROPER SHIPPING NAME | ||||
欧洲陆运危规: | None | |||
国际海运危规: | None | |||
国际空运危规: | None | |||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID: | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IMDG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
欧洲陆运危规 / ER/RID : | None | |||
国际海运危规 / IM0DG: | None | |||
国际空运危规 / IATA-DGR: | None | |||
None | ||||
14.6 特殊防范措施 / SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR USER | ||||
None | ||||
None | ||||
第15部分:法律法规信息 | ||||
适用法规 | ||||
《中华人民共和国安全生产法》、《职业病防治法》、《化学化工实验室安全管理规范》 | ||||
其它的规定 | ||||
《生产安全事故报告和调查处理条例》、《职业病防治法》、《职业安全和卫生法》美国1970 | ||||
第16部分:其他补充信息 | ||||
其他信息 版权所有:BIOFOUNT BEIJING BIO TECH CO.,LTD 公司。许可无限制纸张拷贝,仅限于内部使用。 上述信息视为正确,但不包含所有的信息,仅作为指引使用。本文件中的信息是基于我们目前所知,就正确的安全提示来说适用于本品。该信息不代表对此产品性质的保证。BIOFOUNT公司及其附属公司对任何操作或者接触上述产品而引起的损害不负有任何责任。更多使用条款,参见发票或包装条的反面。 更多销售条款及条件请参见HTTP://WWW.BIO-FOUNT.COM/或发票或装箱单的背面。欲悉详情,请联系:SALES@BIO-FOUNT.COM | ||||
- 相关产品
-
< >
- 推荐产品
-
< >
- 最新产品
-
< >
新闻
怎么做细胞爬片免疫组化染色实验
细胞爬片免疫组化染色,是通过细胞爬片是让玻片浸在细胞培养基内,细胞在玻片上生长,主要用于组织学,免疫组织化学...
2020/7/20 22:04:33
提取病毒RNA的实验方法
提取病毒RNA方法分别有:异硫氰酸胍的提取病毒RNA方法、TRIzol LS提取法、Trizol法提取法等等...
2020/7/22 20:29:26
各种微流控芯片键合方法的优缺点
微流控芯片键合:目前主要有激光焊接、热压键合、胶键合、超音波焊接,每种方法都有各自的优缺点。本文主要介绍聚酯...
2023/7/28 10:43:09

新一代微流控键合解决方案
微流控键合解决方案:微流控芯片制造的一个重要环节,也是最容易被忽视的--芯片键合。其中一个重要因素是:微流控...
2023/7/27 12:44:28
荧光素钾盐使用说明
D-荧光素钾盐(K+)设计用于体外和体内生物发光测定。D-荧光素的质量和纯度对于获得良好和可重复的结果至关重...
2023/7/20 11:05:11
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白)
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白):牛血清白蛋白(BSA)有多种形式,如何选择适合自己的牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是一...
2023/2/14 13:09:18

牛血清白蛋白(BSA)常见问题
牛血清白蛋白(BSA)常见问题:牛血清白蛋白(BSA)在实验室中是通用的,可用于蛋白质印迹、细胞组织培养、P...
2022/10/19 9:39:51
pubmed使用方法(技巧)
pubmed使用方法(技巧):PubMed是一个关于医学问题的学术文章和书籍的数据库。因为它是一份学术期刊,...
2022/10/18 18:06:07
BSA(牛血清白蛋白)
BSA(牛血清白蛋白):牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是一种球状蛋白质,牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是发现于牛血浆中的主要...
2022/10/18 16:48:12
冻干培养细菌的方法
冻干培养细菌的方法:冷冻干燥,也称为冻干或冷冻干燥,是在产品冷冻后除去水分并将其置于真空中的过程。这使得冰可...
2022/10/16 8:27:31




 购物车
购物车 



